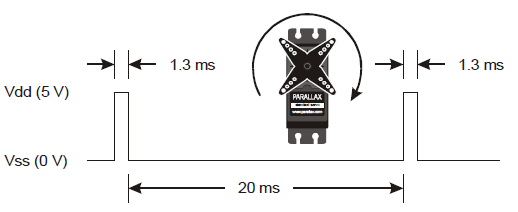
Your cyber:bot servos need to receive a high (5 volt) signal pulse every 20 milliseconds to keep rotating smoothly. The speed and direction of rotation are determined by how long that high pulse lasts. Take a look at the timing diagrams below.
Servo Direction
Full speed clockwise requires 1.3 ms high pulses. To do this, use servo_speed(-75).
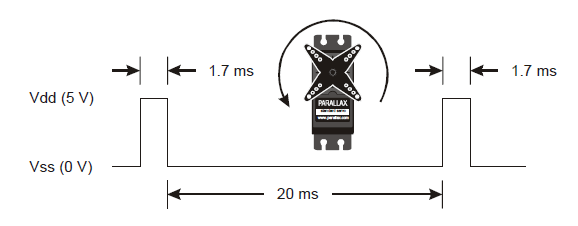
Full speed counter-clockwise requires 1.7 ms high pulses. To do this, use servo_speed(75).
Full speed typically falls in the 50 to 60 RPM range.
To center the servos, we used servo_speed(0). This generates high signals that last 1.5 ms — halfway in between — that not only make the servo stay still, also but resist being twisted. This is useful for stopping on slopes, or pausing in the middle of a series of maneuvers.
To stop sending signals to the servos entirely, use servo_speed(None). This will also make the servos stay still, but they will not resist being twisted.
What’s RPM? Revolutions Per Minute—the number of full rotations turned in one minute.
What’s a pulse train? Just as a railroad train is a series of cars, a pulse train is a series of pulses (brief high signals).
Example Script: left_servo_clockwise
- Put the cyber:bot board power switch in Position 1.
- Make sure your micro:bit has the cyberbot.py module loaded.
- Enter, save, and flash the script left_servo_clockwise.
- Move the power switch to position 2.
- Verify that the left servo is rotating between 50 and 60 RPM clockwise.
# left_servo_clockwise from cyberbot import * bot(18).servo_speed(-75) # 1.3 ms full speed clockwise
Try This: Left Servo Counterclockwise
Now, try turning the left servo the other direction.
- Save the script left_servo_clockwise as left_servo_counterclockwise.
- In the servo_speed function, change (-75) to (75).
- Save the modified script and flash it to the micro:bit.
- Verify that the servo connected to pin 18 now rotates the other direction, which should be counterclockwise, at about 50 to 60 RPM.
Your turn: Left Servo Stay Still
Now, try making the left servo stop, two different ways.
- Rename the script left_servo_clockwise as left_servo_stay_still.
- In the servo_speed function, change (-75) to (0).
- Save the modified script and flash it to the micro:bit.
- Verify that the left servo is not rotating in any direction, but gently resists being twisted.
- Change (0) to (None) and re-flash the code. Verify that the left servo neither turns nor resists being turned.
Example script: right_servo_clockwise
- Open the script left_servo_clockwise.
- Rename the script right_servo_clockwise, and don't forget to update the name in the comment!
- Replace bot(18)with bot(19).
- Run the script and verify that the right servo is rotating between 50 and 60 RPM clockwise.
# right_servo_clockwise from cyberbot import * bot(19).servo_speed(-75) # 1.3 ms full speed clockwise
Try This: Right Servo Counterclockwise
- Rename right_servo_clockwise as right_servo_counterclockwise.
- In bot(19).servo_speed(-75) change (-75) to (75).
- Update the code comments!
- Save the script and flash it to the micro:bit.
- Verify that the pin 19 servo turns full-speed counterclockwise, about 50 to 60 RPM.
Your Turn: Right Servo Stay Still
- In the servo_speed function, change (-75) to (0).
- Save the modified script and flash it to the micro:bit.
- Verify that the right servo is not rotating in any direction, but gently resists being twisted.
- Change (0) to (None) and re-flash the code. Verify that the right servo neither turns nor resists being turned.