Activity 2: Field Testing
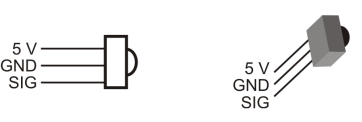
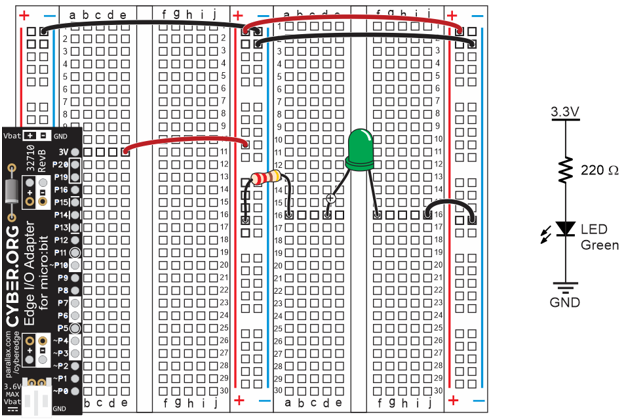
In this activity, you will build and test indicator LEDs that will tell you if an object is detected without the help of the Serial Monitor. This is handy if you are not near a PC or laptop, and you need to troubleshoot your IR detector circuits.