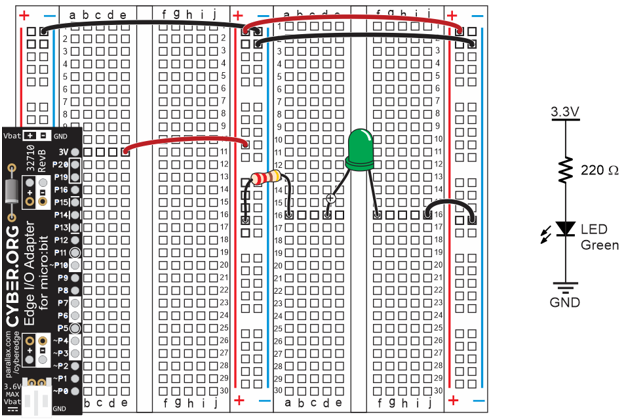
What it’s about
In these activities, you will set up and test your breadboard prototyping system for your micro:bit module. Along the way, you will learn some important circuit building and measuring skills.
Before you start
You will need:
- A What’s a Microcontroller with Python and micro:bit kit (Parallax #32750).
- A computer with a Chrome or Microsoft Edge browser and available USB 2.0 compatible port
Complete these tutorials first:
After You Finish
You will be able to:
- Connect wires and part leads together with a breadboard
- Build circuits on a breadboard
- Test for proper electrical connections, supply levels, and even part values
You will also be ready to move on to the next tutorial (coming soon!)
