Item code: 29133
What It Can Do
- Measures the earth’s magnetic field in three axes, with a 1–2 degree accuracy
- Provides individual readings for each axis, which may be used separately or together for 3D calculations
- Measures raw strength (gauss) of a nearby magnetic source
The 3-Axis Compass module measures magnetic fields in three directions – or axes, labeled X, Y, and Z. In its most simple form, the module can be used as a basic compass to find earth’s magnetic north.
The compass module can also sense the relative strength of a nearby magnetic source, such as those caused by magnets or electric fields. As the sensor detects magnetism in three dimensions, it can determine relative distance and direction to these sources.

The compass is commonly used with a multi-axis accelerometer, where the data from both sensors can provide useful information detailing speed and direction of travel. The Memsic 2125 Dual-axis Accelerometer and MMA7455 3-Axis Accelerometer Module are good companion accelerometers for the 3-Axis Gyroscope module
It may also be used with an accelerometer and 3-axis gyroscope to construct a 9-axis IMU (intertial measurement unit), common in unmanned aerial vehicles, such as drones and quadcopters.
Parts List
- 3-Axis Compass module
- BASIC Stamp HomeWork Board, Propeller BOE, Propeller QuickStart, or Arduino Uno microcontroller (with breadboard, as needed)
- 22 gauge solid conductor hookup wire
Basic Wiring

- Power Requirements: 2.7 to 6.5 VDC
- Communication Interface: I2C (up to 400 kHz)
- Dimensions: 0.725 x 0.650 in (1.8 x 1.7 cm)
Program KickStarts
The KickStart examples display raw data output for each of the three axes. Values are retrieved from the module using the I2C interface.
BASIC Stamp HomeWork Board

Download BASIC Stamp 2 code for the Compass Module
' {$STAMP BS2}
' {$PBASIC 2.5}
SDA PIN 0 ' SDA of compass to pin P0
SCL PIN 1 ' SCL of compass to pin P1
WRITE_Data CON $3C ' Requests Write operation
READ_Data CON $3D ' Requests Read operation
MODE CON $02 ' Mode setting register
X_MSB CON $03 ' X MSB data output register
X VAR Word
Y VAR Word
Z VAR Word
rawl VAR Word
rawh VAR Word
' Variables for I2C communications
I2C_DATA VAR Byte
I2C_LSB VAR Bit
I2C_REG VAR Byte
I2C_VAL VAR Byte
PAUSE 100 ' Power up delay
I2C_REG = MODE ' Set operating mode to continuous
I2C_VAL = $0
GOSUB I2C_Write_Reg
DO
GOSUB GetRawReading ' Get raw Compass reading
DEBUG HOME, "X = ",11, SDEC x, CR ' Print values
DEBUG "Y = ",11, SDEC y, CR
DEBUG "Z = ",11, SDEC z, CR
DEBUG CR
LOOP
GetRawReading:
PAUSE 400 ' Wait for new data
' Send request to X MSB register
GOSUB I2C_Start
I2C_DATA = WRITE_Data
GOSUB I2C_Write
I2C_DATA = X_MSB
GOSUB I2C_Write
GOSUB I2C_Stop
'Get data from register (6 bytes total, 2 bytes per axis)
GOSUB I2C_Start
I2C_DATA = READ_Data
GOSUB I2C_Write
' Get X
GOSUB I2C_Read
rawH = I2C_Data
GOSUB I2C_ACK
GOSUB I2C_Read
rawL = I2C_Data
GOSUB I2C_ACK
X = (rawH << 8) | rawL
' Get Z
GOSUB I2C_Read
rawH = I2C_Data
GOSUB I2C_ACK
GOSUB I2C_Read
rawL = I2C_Data
GOSUB I2C_ACK
Z = (rawH << 8) | rawL
' Get Y
GOSUB I2C_Read
rawH = I2C_Data
GOSUB I2C_ACK
GOSUB I2C_Read
rawL = I2C_Data
GOSUB I2C_NACK
Y = (rawH << 8) | rawL
GOSUB I2C_Stop
RETURN
'---------I2C functions------------
' Set I2C_REG & I2C_VAL before calling this
I2C_Write_Reg:
GOSUB I2C_Start
I2C_DATA = WRITE_DATA
GOSUB I2C_Write
I2C_DATA = I2C_REG
GOSUB I2C_Write
I2C_DATA = I2C_VAL
GOSUB I2C_Write
GOSUB I2C_Stop
RETURN
' Set I2C_REG before calling this, I2C_DATA will have result
I2C_Read_Reg:
GOSUB I2C_Start
I2C_DATA = WRITE_DATA
GOSUB I2C_Write
I2C_DATA = I2C_REG
GOSUB I2C_Write
GOSUB I2C_Stop
GOSUB I2C_Start
I2C_DATA = READ_DATA
GOSUB I2C_Write
GOSUB I2C_Read
GOSUB I2C_NACK
GOSUB I2C_Stop
RETURN
I2C_Start:
LOW SDA
LOW SCL
RETURN
I2C_Stop:
LOW SDA
INPUT SCL
INPUT SDA
RETURN
I2C_ACK:
LOW SDA
INPUT SCL
LOW SCL
INPUT SDA
RETURN
I2C_NACK:
INPUT SDA
INPUT SCL
LOW SCL
RETURN
I2C_Read:
SHIFTIN SDA, SCL, MSBPRE, [I2C_DATA]
RETURN
I2C_Write:
I2C_LSB = I2C_DATA.BIT0
I2C_DATA = I2C_DATA / 2
SHIFTOUT SDA, SCL, MSBFIRST, [I2C_DATA7]
IF I2C_LSB THEN INPUT SDA ELSE LOW SDA
INPUT SCL
LOW SCL
INPUT SDA
INPUT SCL
LOW SCL
RETURN
When this program is run, the BASIC Stamp Debug Terminal will automatically open.
Propeller BOE and Propeller QuickStart
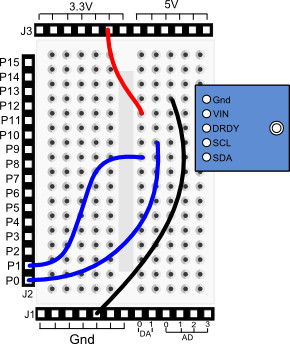
Propeller BOE Wiring Diagram
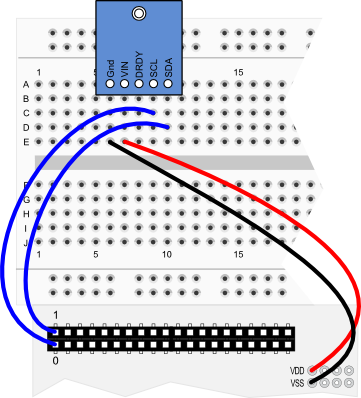
Propeller QuickStart Wiring Diagram
Download Propeller Spin code for the Compass Module
OBJ
pst : "FullDuplexSerial" ' Comes with Propeller Tool
CON
_clkmode = xtal1 + pll16x
_clkfreq = 80_000_000
datapin = 1 ' SDA of compass to pin P1
clockPin = 0 ' SCL of compass to pin P0
WRITE_DATA = $3C ' Requests Write operation
READ_DATA = $3D ' Requests Read operation
MODE = $02 ' Mode setting register
OUTPUT_X_MSB = $03 ' X MSB data output register
VAR
long x
long y
long z
PUB Main
waitcnt(clkfreq/100_000 + cnt) ' Power up delay
pst.start(31, 30, 0, 115200)
SetCont
repeat
SetPointer(OUTPUT_X_MSB)
getRaw ' Gather raw data from compass
pst.tx(1)
ShowVals
PUB SetCont
' Sets compass to continuous output mode
start
send(WRITE_DATA)
send(MODE)
send($00)
stop
PUB SetPointer(Register)
' Start pointer at user specified register (OUT_X_MSB)
start
send(WRITE_DATA)
send(Register)
stop
PUB GetRaw
' Get raw data from continuous output
start
send(READ_DATA)
x := ((receive(true) << 8) | receive(true))
z := ((receive(true) << 8) | receive(true))
y := ((receive(true) << 8) | receive(false))
stop
~~x
~~z
~~y
x := x
z := z
y := y
PUB ShowVals
' Display XYZ compass values
pst.str(string("X="))
pst.dec(x)
pst.str(string(", Y="))
pst.dec(y)
pst.str(string(", Z="))
pst.dec(z)
pst.str(string(" "))
PRI send(value)
value := ((!value) >< 8)
repeat 8
dira[dataPin] := value
dira[clockPin] := false
dira[clockPin] := true
value >>= 1
dira[dataPin] := false
dira[clockPin] := false
result := !(ina[dataPin])
dira[clockPin] := true
dira[dataPin] := true
PRI receive(aknowledge)
dira[dataPin] := false
repeat 8
result <<= 1
dira[clockPin] := false
result |= ina[dataPin]
dira[clockPin] := true
dira[dataPin] := aknowledge
dira[clockPin] := false
dira[clockPin] := true
dira[dataPin] := true
PRI start
outa[dataPin] := false
outa[clockPin] := false
dira[dataPin] := true
dira[clockPin] := true
PRI stop
dira[clockPin] := false
dira[dataPin] := false
To view the results of the demonstration, after uploading is complete run the Parallax Serial Terminal from the Run menu or press F12. Click the Enable button, and momentarily depress the Reset button on the Propeller QuickStart board to restart the program.
Arduino Uno

Download Arduino Code for the Compass Module
#include <Wire.h>
#define Addr 0x1E // 7-bit address of HMC5883 compass
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
delay(100); // Power up delay
Wire.begin();
// Set operating mode to continuous
Wire.beginTransmission(Addr);
Wire.write(byte(0x02));
Wire.write(byte(0x00));
Wire.endTransmission();
}
void loop() {
int x, y, z;
// Initiate communications with compass
Wire.beginTransmission(Addr);
Wire.write(byte(0x03)); // Send request to X MSB register
Wire.endTransmission();
Wire.requestFrom(Addr, 6); // Request 6 bytes; 2 bytes per axis
if(Wire.available() <=6) { // If 6 bytes available
x = Wire.read() << 8 | Wire.read();
z = Wire.read() << 8 | Wire.read();
y = Wire.read() << 8 | Wire.read();
}
// Print raw values
Serial.print("X=");
Serial.print(x);
Serial.print(", Y=");
Serial.print(y);
Serial.print(", Z=");
Serial.println(z);
delay(500);
}
To view the results of the demonstration, after uploading is complete click the Serial Monitor icon in the Arduino IDE. This displays the Serial Monitor window. Momentarily depress the Reset button on the Arduino board to restart the sketch.
For More Information
- 3-Axis Compass (#29133) data sheet and application notes
- More information on magnetometers and other forms of digital compasses may be found on Wikipedia: Magnetometer
- Combine the 3-axis compass with the Memsic 2125 Dual-Axis Accelerometer, or MM7455 3-Axis Accelerometer
- Combine the 3-axis compass with the Parallax MMA7455 3-Axis Accelerometer Module and Gyroscope Module 3-Axis L3G4200D to create a 9-axis inertial momentum unit (IMU)