Test Activity Board Arlo’s Encoder Connections
The Arlo has encoders that track distance in 144th increments of a full wheel rotation. These increments are commonly called “counts”, and the Arlo’s encoders send 144 counts per revolution. The Arlo’s encoders are quadrature, meaning that the two encoder sensors are offset by ¼ of a count. By monitoring the pattern of low-high-low transitions for both sensors, the DHB-10 can also determine which direction the wheel is turning. For a given wheel, 144 counts would mean a full forward rotation, and -144 counts would mean a full backward rotation.
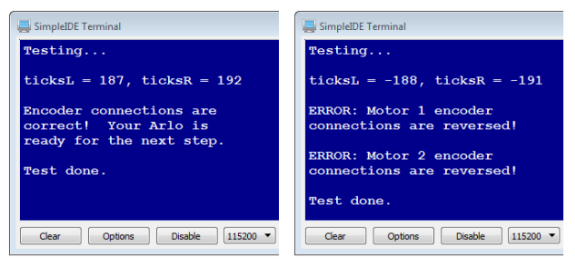
The next program will display the status of your encoder connections in the SimpleIDE Terminal. If there is a problem, it may indicate that the encoder cables have been swapped or that there is some other wiring problem. Here are examples of what you might see:
- We want the wheels to be able to spin freely during this test, so set your Arlo on a box, stands, or some other stable platform that prevents its wheels from coming into contact with the table top.
- Open Test Encoder Connections.side and click “Run with Terminal”.
- Check the SimpleIDE Terminal’s messages. It’ll either tell you that the Arlo is ready for the next step, or describe the error it encountered and suggest either a fix, or at least where to look for a potential problem.
/*
Arlo - Test Encoder Connections.c
This program tests to make sure the Arlo's wheel encoder connections
are correct. The Arlo will not be ready for the next step until you
have verified that the number of encoder transitions (ticks) for both
wheels are positive when the wheels roll forward.
If you have not already completed Test Arlo Motor Connections.c,
complete it first, then continue from here.
Use SimpleIDE's Run with Terminal button to run this program. If the
SimpleIDE Terminal displays the "Encoder connections are correct!..."
message, your Arlo is ready for the next step, which is running
navigation programs.
If the SimpleIDE Terminal instead displays one or more "ERROR..."
messages, those encoder encoder connections will need to be
corrected. For example, if the messages says, "ERROR: Motor 1
encoder connections are reversed!", you will need to unplug and
swap the two 3-wire encoder cables next to the Motor 1 terminal
on the DHB-10, swap them, and plug them back in.
Make sure to test between each adjustment. Your arlo will not be
ready for the next step until you get the success message from
this test.
*/
#include "simpletools.h" // Include simpletools library
#include "arlodrive.h" // Include arlodrive library
int ticksL, ticksR; // Encoder tick counts
int main() // Main function
{
print("Testing...\n\n"); // Display status
drive_feedback(0); // Disable encoder feedback
drive_clearTicks(); // Clear encoder values
drive_speed(32, 32); // Drive motors at 1/4 power
pause(4000); // ...for 4 seconds
drive_speed(0, 0); // Cut power to motors
drive_getTicks(&ticksL, &ticksR); // Get encoder measurements
print("ticksL = %d, ticksR = %d\n\n", // Display encoder measurements
ticksL, ticksR);
if((ticksL > 175) && (ticksL < 325) && // Both distances positive?
(ticksR > 175) && (ticksR < 325))
{
print("Encoder connections are \n"); // Success message
print("correct! Your Arlo is \n");
print("ready for the next step.\n\n");
}
else
{
if(ticksL > 175 && ticksL < 325) // Left encoders cables correct?
{
print("Motor 1 encoder cables \n"); // Correct encoder message
print("are connected correctly.\n\n");
}
else if(ticksL > -325 && ticksL < -125) // Left encoders cables swapped?
{
print("ERROR: Motor 1 encoder \n"); // Swapped encoder message
print("connections are reversed!\n\n");
}
else // Other problem
{
print("ERROR: Motor 1 encoder \n"); // Other encoder error message
print("values out of range. \n");
print("Recheck encoder connections\n");
print(" and assemblies.\n\n");
}
if(ticksR > 175 && ticksR < 325) // Right encoders cables correct?
{
print("Motor 2 encoder cables\n"); // Correct encoder message
print("are connected correctly.\n\n");
}
else if(ticksR > -325 && ticksR < -125) // Right encoders cables swapped?
{
print("ERROR: Motor 2 encoder\n"); // Swapped encoder message
print("connections are reversed!\n\n");
}
else // Other problem
{
print("ERROR: Motor 2 encoder\n"); // Other encoder error message
print("values out of range.\n");
print("Recheck encoder connections\n");
print("and assemblies.\n\n");
}
}
print("Test done.\n\n"); // Display status
}
