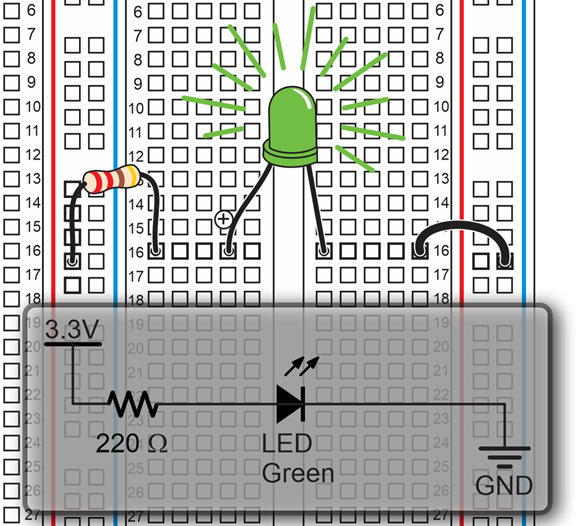
How the LED Circuit Works
About the LED
The term LED is an abbreviation for Light Emitting Diode. When current flows through an LED, it emits light. It glows more brightly with more current, and less brightly with less current. That takes care of “light emitting”, now what is a diode? A diode is a one-way valve for electric current. In other words, current can only flow through in one direction. That’s why it’s important to make sure the longer pin is in (d, 16) and the shorter pin is in (f, 16). If the pins are reversed, no current will flow, and the LED will not emit light. The longer (+) pin is called the anode and the shorter one is the cathode.
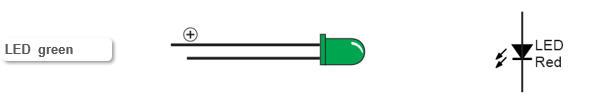
No longer pin? If an LEDs pins get cut to the same length, there’s a flat spot on the round plastic case next to the cathode pin to help identify it.
About the Resistor
A resistor “resists” the flow of current. Resistance is measured in ohms and abbreviated with the greek letter omega (Ω). Most resistors have color bands that indicate what their resistance values are. More on that later.
The 220 Ω resistor in this activity limits the current through the LED to about 5 mA, which is 5/1000 of an amp. The maximum current for these LEDs is 20 mA. Larger values of resistance will let less current flow, making the LED dimmer. Likewise, smaller resistance values will let more current flow through, making the LED brighter.
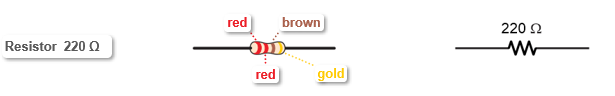
Resistors plug in either way. Unlike diodes, you won’t have to worry about what direction to connect a resistor. Resistors resist current the same amount in either direction.
By connecting one end of the LED circuit to 3.3 V and the other end to GND (0 V), the electrical pressure propelling current (electron flow) through the LED circuit is 3.3 V.