Meet the Terminal
The serial monitor terminal apps that are built into python.microbit.org online editor and the Mu software give you two ways to interact with your micro:bit:
- In Serial mode, the micro:bit can run a script that sends messages to your computer which are displayed by the terminal. Depending on the script, the micro:bit can also store and process messages you type into the terminal.
- The micro:bit can host REPL (Read-Evaluate-Print-Loop) mode, which is for typing MicroPython statements into the terminal and seeing immediate results — no flashing a script required.

Most of the Cybersecurity tutorials will use the serial monitor to interact with a micro:bit while its scriptis running. For example, if the micro:bit picks up any radio messages, it will be able to display them quickly in the serial monitor. For the cyber:bot, it is also useful for testing sensor circuits before relying on them for navigation.
Why is it called a terminal?
The serial monitor is a kind of terminal. In computing, a terminal is “A combination of a keyboard and output device (such as a video display unit) by which data can be entered into or output from a computer or electronic communications system” according to Merriam Webster.
Large computers with numerous “terminals” connected to them used to be common in business and academics. Each terminal had a monitor and keyboard, and sometimes other devices.
 Image source: “DEC VT100” by Gorthmog is licensed under CC BY-SA 4.0
Image source: “DEC VT100” by Gorthmog is licensed under CC BY-SA 4.0
With the advent of more sophisticated computers and networks, terminal emulator apps like the Windows command prompt became common.
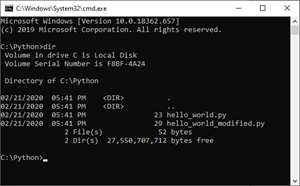
The “terminals” built into python.microbit.org and Mu are also considered computer terminal emulator apps, even though they are communicating with a microcontroller.
Hardware terminals are still in use today. For example, an ATM (Automated Teller Machine) is a terminal that’s connected to the bank’s system. At the ATM, a user can access their bank account and interact with a bank to withdraw or deposit money, check account balances, etc.
 Image source: “ATM_750x1300.jpg” by Rfc1394 is released into Public Domain
Image source: “ATM_750x1300.jpg” by Rfc1394 is released into Public Domain
