Add Obstacle Detection
The script IR_Remote_Control.py makes your cyber:bot drive in whatever direction you send it — even into walls. If you have a Ping))) sensor, you can give your ’bot a bit of self-preservation behavior.
Additional parts needed:
- Ping))) Ultrasonic Distance Sensor (#28015)
- 2.2 k-ohm resistor from your robot’s Electronic Component Pack
- Jumper wires
The Ping))) sensor can go directly into the breadboard.
- Add the Ping))) sensor to the cyber:bot and connect its signal pin to P8, as shown below. You may need to re-position the IR receiver, but that is fine as long as its signal pin still connects to P10.
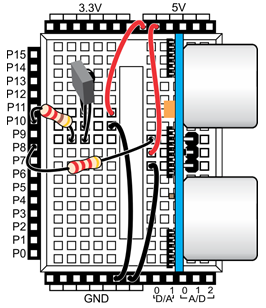
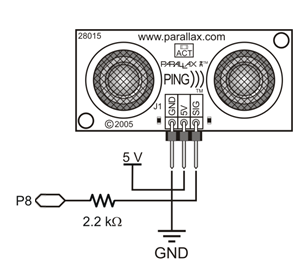
The script IR_Remote_Control_with_Ping is just an expansion of the original. Up top, it adds from ping import *. Then, it takes the entire contents of the while True: loop and wraps it in a nested conditional while loop. This inner loop only executes while (ping(8).distance(’cm’)) > 15:. If that condition is not true, meaning you have driven your cyber:bot close too an object, some new lines of code at the bottom of the conditional loop make the cyber:bot express its surprise and turn away until the obstacle is no longer detected.
- You will need to add the ping.py module to your project, just like you added the cyberbot.py and tv_remote.py before testing the remote.
- Change the project’s name from ir_remote_control to ping_servo_test.
- Enter the script below, and then click Save.
- Click Send to micro:bit.
- Disconnect the cyber:bot robot’s USB cable, and set it on the floor.
- Set the cyber:bot board’s PWR switcht to 2 and
# ir_remote_control_with_ping
from cyberbot import *
from tv_remote import *
from ping import *
wL = 0
wR = 0
img = Image.HAPPY
bot(22).tone(2000, 300)
while True:
while (ping(8).distance('cm')) > 15:
num = ir(10).remote()
if num == 1:
wL = 0
wR = -75
img = Image.ARROW_SE
elif num == 2:
wL = 75
wR = -75
img = Image.ARROW_S
elif num == 3:
wL=75
wR=0
img=Image.ARROW_SW
elif num == 4:
wL=-75
wR=-75
img=Image.ARROW_E
elif num == 5:
wL=0
wR=0
img=Image.HAPPY
elif num == 6:
wL=75
wR=75
img=Image.ARROW_W
elif num == 7:
wL=0
wR=75
img=Image.ARROW_NE
elif num == 8:
wL=-75
wR=75
img=Image.ARROW_N
elif num == 9:
wL=-75
wR=0
img=Image.ARROW_NW
display.show(img)
bot(18).servo_speed(wL)
bot(19).servo_speed(wR)
display.show(Image.SURPRISED)
bot(18).servo_speed(-50)
bot(19).servo_speed(-50)
bot(22).tone(500, 1000)
