Apply Caesar Cipher to Words from Serial Monitor
This script places the Caesar cipher in a loop. This will allow you to type entire words for encrypting/decrypting! It still also works with single characters if that’s all you want to encrypt.
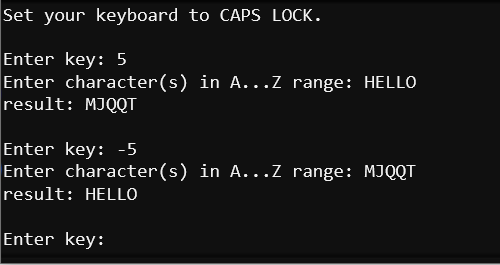
Example script: caesar_terminal_words
- Change project’s name from caesar_terminal_letters to caesar_terminal_words.
- Update it to match the script below
- Save the modified script.
- Click the Send to micro:bit button.
# caesar_terminal_words
from microbit import *
sleep(1000)
print("Set your keyboard to CAPS LOCK.")
print()
while True:
text = input("Enter key: ")
key = int(text)
word = input("Enter character(s) in A...Z range: ")
alpha = "ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ"
result = "
for letter in word:
letter = letter.upper()
index = ( alpha.find(letter) + key ) % 26
result = result + alpha[index]
print("result:", result)
print()
- Follow the prompts in the serial monitor. Valid keys are from -25 to 25.
- Try encrypting HELLO with the key set to 5.
- Try decrypting MJQQT with the key set to -5.
- Write a short message for your friend or lab partner and give them the key to decrypt it.
How caesar_terminal_words Works
Inside the while True loop, the script stores a number you enter into an int variable named key. Then, it stores a word you type in a string variable named word.
text = input("Enter key: ")
key = int(text)
word = input("Enter character(s) in A...Z range: ")
In addition to the alpha (alphabet) string, a second empty string named result is created to store the result.
alpha = "ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ"
result = "
After that, a for… loop goes through each letter in the plaintext string. After making sure the letter is upper-case, it applies the Caesar cipher with two lines. The first finds the index of the new character with index = ( alpha.find(letter) + key ) % 26. The second adds the character to whatever is already in the ciphertext string with result = result + alpha[index].
for letter in word:
letter = letter.upper()
index = ( alpha.find(letter) + key ) % 26
result = result + alpha[index]
Before repeating the loop, the ciphertext is printed to the terminal.
print("result: ", result)
