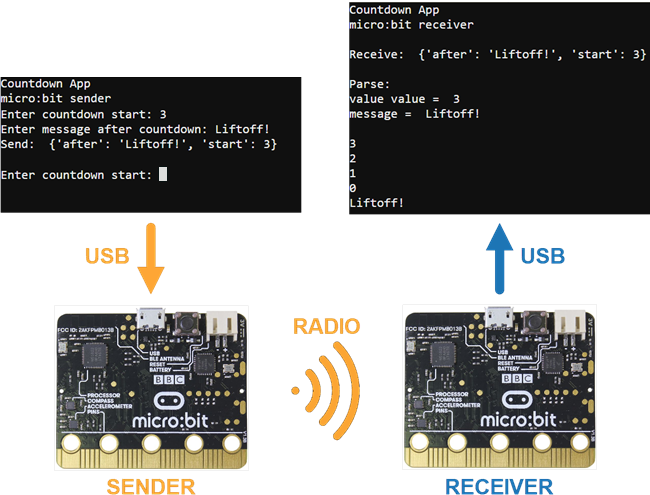
Send and Receive Packets
The sender micro:bit and receiver micro:bit each have their own script, and they must be running at the same time.
- Connect two micro:bit modules to two USB ports with two USB cables.
- Open two separate browsers and navigate both to python.microbit.org.
- In each micro:bit Python Editor, click the three dots ⋮ by the Send to micro:bit button, select Connect, and then set up each micro:bit connection.
- If you are part of a class, and have been assigned a channel, make sure to adjust the script’s channel=7 to your assigned channel before you save and flash the scripts.
- Enter, name, save, and flash the sender script countdown_sender into the sending micro:bit.
(See Save & Edit Scripts and Flash Scripts with Python Editor.) - Enter, name, save, and flash the receiver script countdown_reciever into the receiving micro:bit. It’s below the countdown_sender script.
Example Sender Script: countdown_sender
# countdown_sender
from microbit import *
import radio
radio.on()
radio.config(channel=7,length=50)
sleep(1000)
print("Countdown App")
print("micro:bit sender")
while True:
text = input("Enter countdown start: ")
value = int(text)
message = input("Enter message after countdown: ")
dictionary = { }
dictionary['start'] = value
dictionary['after'] = message
packet = str(dictionary)
print("Send: ", packet)
radio.send(packet)
print()
Example Receiver Script: countdown_receiver
# countdown_receiver
from microbit import *
import radio
radio.on()
radio.config(channel=7,length=50)
sleep(1000)
print("Countdown App")
print("micro:bit receiver\n")
while True:
packet = radio.receive()
if packet is not None:
print("Receive: ", packet)
print()
print("Parse: ")
dictionary = eval(packet)
value = dictionary['start']
message = dictionary['after']
print("value = ", value)
print("message = ", message, "\n")
while value >= 0:
print(value)
sleep(1000)
value = value - 1
print(message)
print()
- Click Show serial in both browsers.
- Follow the prompts in the sender micro:bit’s serial monitor for entering the countdown start value and the message to display afterwards.
- Check the receiver micro:bot’s serial monitor and verify that it completes the countdown and displays the message you entered.