How Measuring Rotation Angles Works
In addition to the microbit module, this project has to import the math module, which contains common trigonometry methods. Then, pause (1000) gives the terminal a second to set up communication with the micro:bit before it has to display any messages.
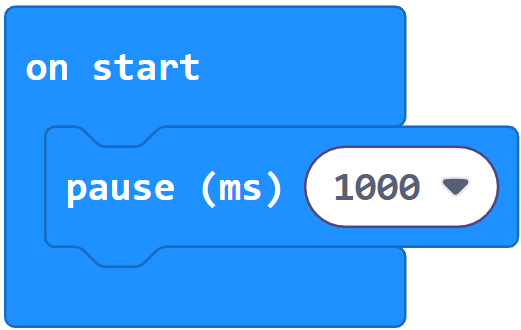
In the main loop, the x and y axis accelerometer measurements are stored in variables named x and y.
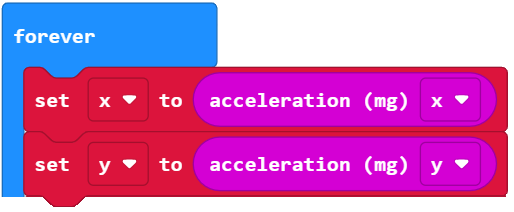
The next block performs a calculation called arctangent. If you have never heard of it, the next page explains it.
The block atan2(x, y) is what returns the angle result, but that result is in radians—a different kind of angle measurement where a half circle is approximately 3.14, or Pi (π), radians instead of 180°. To convert radians to degrees in blocks, use the (…) x 57.296, this is the approximate number that is multiplied by radians to get the degrees.*

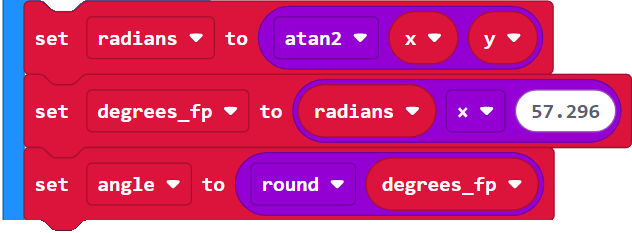
Another way to think about the block above is to break it into steps, each in an individual block. For example:
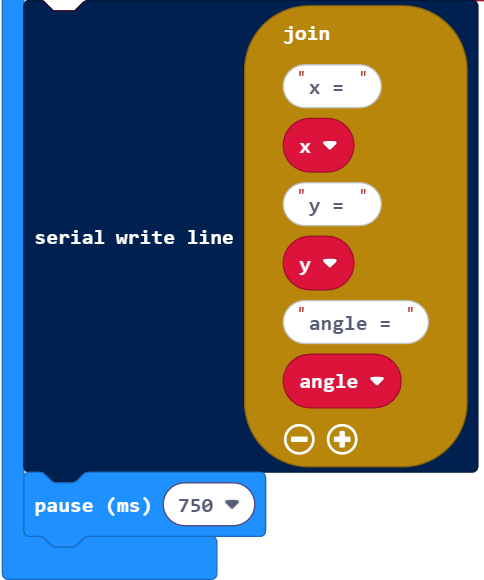
Now that the angle is calculated, the project displays labels for each variable, followed by its value.
*Alternately, the project could multiply by 180 and divide by pi. At this point, there’s a floating point result, and the round block will round to the nearest integer. For example, if the result was 179.5 or higher, it would round to 180. If the value was instead between 179 and 179.499…., it would round to 179 instead.
