Share Something Personal – Encrypted!
In this activity, you will examine the effects of encrypting your messages on a sniffing cyberattack. You will leave the sniffer micro:bit’s script the same receiver script, but add Caesar cipher encryption to the transmitter and intended receiver scripts.
Cybersecurity: Encryption Intro has activities introducing the Caesar cipher if you want to learn more about it.
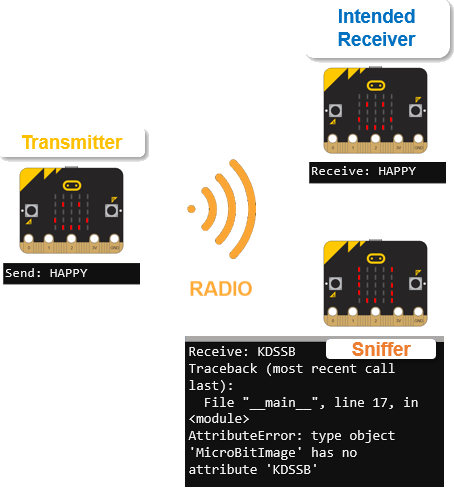
- Repeat the setup from the previous activity, Share Something Personal -Unencrypted.
- Enter, name, save, and flash the radio_send_images_caesar transmitter script into the micro:bit you chose as the transmitter—the one sending the HAPPY/SAD/ANGRY images.
- The micro:bit you chose to be the sniffer should still be running the radio_receive_images receiver script from the previous activity.
- Enter, name, save, and flash the radio_receive_images_caesar receiver script into the micro:bit you chose to be the intended receiver. The receiver script is below the transmitter script.
- Remember, if you only have two micro:bit modules, you can enter flash, save and test the intended receiver script after testing the sniffer.
Transmitter Script: radio_send_images_caesar
# radio_send_images_caesar.py
from microbit import *
import radio
''' Function converts plaintext to ciphertext using key '''
def caesar(key, word):
alpha = "ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ"
result = "
for letter in word:
letter = letter.upper()
index = ( alpha.find(letter) + key ) % 26
result = result + alpha[index]
return result
''' Script starts from here... '''
radio.on()
radio.config(channel=7)
sleep(1000)
string_list = ["HAPPY", "SAD", "ANGRY"]
while True:
for packet in string_list:
print("packet:", packet)
display.show(getattr(Image, packet))
packet = caesar(3, packet)
print("Send encrypted:", packet)
radio.send(packet)
sleep(2500)
Receiver Script: radio_receive_images_caesar
# radio_receive_images_caesar.py
from microbit import *
import radio
''' Function converts plaintext to ciphertext using key '''
def caesar(key, word):
alpha = "ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ"
result = "
for letter in word:
letter = letter.upper()
index = ( alpha.find(letter) + key ) % 26
result = result + alpha[index]
return result
''' Script starts from here... '''
radio.on()
radio.config(channel=7)
sleep(1000)
while True:
packet = radio.receive()
if packet:
print("Receive encrypted:", packet)
packet = caesar(-3, packet)
print("packet:", packet)
display.show(getattr(Image, packet))
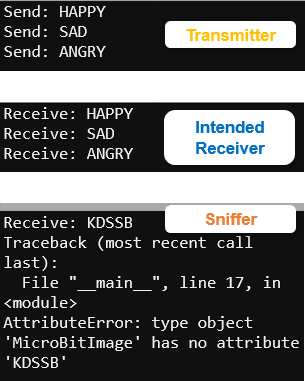
Test Sniffer and Intended Receiver Responses
- Click the Show serial button in any of the browsers where the serial monitor is not already open.
- Compare the intended receiver micro:bit’s terminal to the sniffer’s terminal.
- In this case, the KDSSB instead of HAPPY should cause an exception. You will correct this in the upcoming activities.
- Compare the intended receiver micro:bit’s LED display to the sniffers as well.
- Reminder: If you are only using two micro:bit modules, test the sniffer first while it’s running the previous activity’s receiver script. Then, load this activity’s receiver script and compare the difference.