Try This: Improve the Script
Try This – Prove it Works
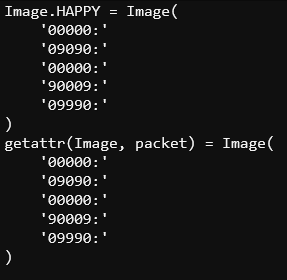
If you’re skeptical that packet = “HAPPY” followed by getattr(Image, packet) is equivalent to Image.HAPPY, try this:
- Add this routine between sleep(1000) and while True: in the transmitter script radio_send_images.py.
- Flash the modified script with the Send to micro:bit button.
print("Image.HAPPY =", Image.HAPPY)
sleep(500)
packet = "HAPPY"
print( "getattr(Image, packet) =", getattr(Image, packet) )
sleep(500)
- If the serial monitor isn’t already open, click Show serial.
- Verify that the results resemble what’s shown here.
Image(…) has brightness data for each LED in the display. In this case it only uses 0 (LED off), and 9 (LED brightest). Values between 0 and 9 for each LED can be used to control the brightness.
Your Turn – Compact your Code
This code takes up unnecessary program space in the micro:bit module’s memory.
packet = "HAPPY"
print("Send:", packet)
radio.send(packet)
sleep(2500)
packet = "SAD"
print("Send:", packet)
radio.send(packet)
sleep(2500)
packet = "ANGRY"
print("Send:", packet)
radio.send(packet)
sleep(2500)
Your program can instead create a list like string_list = [“HAPPY”, “SAD”, “ANGRY”]. Then, inside the while True loop, the for packet in string_list can index through each string in string_list.
- Use that hint to modify the radio_send_images transmitter script.
- Test and verify your solution.
