How it Works
How the Ammeter Works
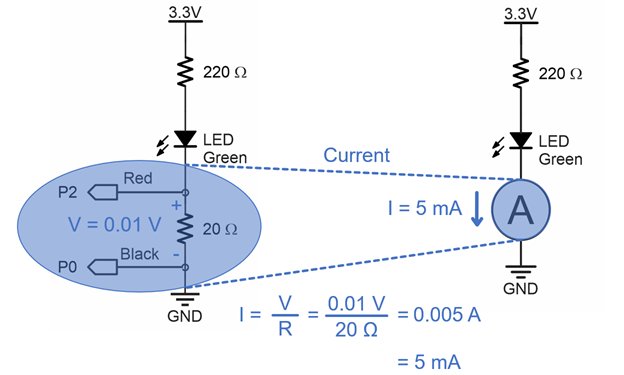
The micro:bit, Python script, CYBERscope, 20 Ω resistor, and alligator clip probes all work together to emulate a common multimeter running in ammeter mode. Keep in mind that something akin to the 20 Ω resistor is inside the ammeter. You would not be adding it to the circuit, just connecting the multimeter’s probes in series, just like you did with the alligator clip probes.
The ammeter script’s multimeter module measures the voltage across the 20 Ω resistor by subtracting the voltage measured at P0 from the voltage measured at P2. The multimeter module’s ammeter function then uses I = V / R to calculate current from voltage and resistance. For example, if V is 0.01 V and R is 20 Ω, then I = V / R = 0.01 V / 20 Ω = 0.005 A = 5 mA.
Did You Know?
I = V / R is one of the three forms of the Ohm’s law equations, which you will experiment with in the next activity.
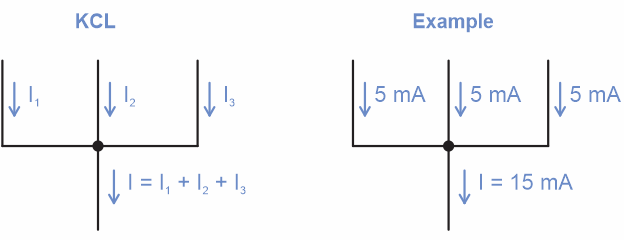
Kirchhoff’s current law (abbreviated KCL):
“For any node (junction) in an electrical circuit, the sum of currents flowing into that node is equal to the sum of currents flowing out of that node.” [1]
For example, if the current from three parallel circuits feeds into a single circuit, the current in that single circuit would be the sum of the three currents. In equation terms, three circuits would be:
I = I1 + I2 + I3
… for some number of n circuits, you’d add all of them up:
I = I1 + I2 + … + In
1. Wikipedia. 2021. “Kirchhoff’s circuit laws.” Wikipedia The Free Encyclopedia.
