Adjust the Detection Range
When it is dark outside, you may have noticed that a brighter flashlight lets you see objects that are further away. By making the cyber:bot’s infrared LED headlights brighter, you can also increase its detection range. A smaller resistor allows more current to flow through an LED. More current through an LED is what causes it to glow more brightly. In this activity, you will examine the effect of different resistance values with both the red and infrared LEDs.
Parts List
(2) Resistors, 470 Ω (yellow-violet-brown)
(2) Resistors, 220 Ω (red-red-brown)
(2) Resistors, 1 kΩ (brown-black-red)
(2) Resistors, 4.7 kΩ (yellow-violet-red)
(1) Red LED
(1) Misc. Jumper Wire
Piece of white paper
Ruler
LED Brightness
First, let’s use a red LED to actually see the difference that a resistor makes in how brightly an LED glows. All we need to test the LED circuit is a script that sends a high signal to an LED.
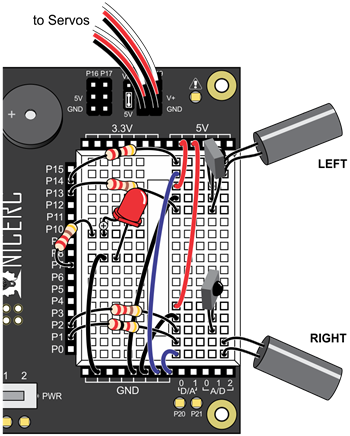
- Leave all the current IR object detector circuits in place.
- Put the cyber:bot board’s power switch in position 0.
- Add a red LED circuit connected to P7.

Example script: P7_led_on
- Use the micro:bit Python Editor to open a previous cyber:bot project, like IR_interference_sniffer or cyberbot-template-with-blink.
- Set the project’s name to P7_led_on, update the script so that it matches the one below, and then click Save.
- Click Send to micro:bit.
# P7_led_on from cyberbot import * bot(7).write_digital(1)
- Put the cyber:bot board’s PWR switch in position 1.
- Verify that the LED in the circuit connected to P7 emits light.
Try this: Test LED Brightness with Different Resistors
- As you work, put set the cyber:bot board’s PWR switch to position 0 for changing resistors, and to position 1 for running the test. When you set the PWR switch back to 1, the same script will run, so you can pick up right where you left off with each test.
- Replace the 220 Ω resistor that goes from pin 7 to the LED’s cathode with a 470 Ω resistor. Note now how brightly the LED glows.
- Repeat with a 1 kΩ resistor. Is the red LED brighter or dimmer?
- Repeat once more with a 4.7 kΩ resistor. Now how bright, or dim, is the red LED?
- You can remove the 4.7 kΩ resistor, red LED, and jumper wire before moving on to the next portion of this activity.
- Explain in your own words the relationship between LED brightness and series resistance.
