Test the IR Object Detectors
Detecting Objects with Infrared
Object detection with the IR LED and receiver circuits you built on your cyber:bot takes three steps:
- Flash the IR LED on/off at 37500 Hz.
- Delay for a millisecond or more. This gives the IR receiver time to send a low signal if it detects 37500 Hz, that is 37.5 kHz, IR light reflecting off an object.
- Check the state of the IR receiver for either a high signal (no IR detected), or a low signal (IR detected).
The function ir_detect handles all of these steps for us. Here is an example from our next script:
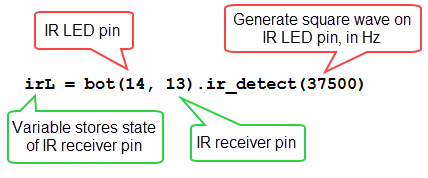
The ir_detect function generates a square wave on the IR LED pin; here the arguments specify a 37500 Hz signal on P14. This square wave last about 2 milliseconds. Then, the function checks the state of the IR receiver pin; P13 in this example, and stores the result in the variable irL. The state of the IR receiver pin. IR receiver detects a reflection of the 37500 Hz infrared light signal, irL will store a zero, and if not, irL will store a 1— remember that this receiver is an “active low” sensor.
Hardware Setup
- Set the cyber:bot board’s power (PWR) switch to Position 0.
- Make sure the battery holder is loaded with 5 AA batteries.
- Make sure the battery holder’s barrel plug is firmly plugged into the cyber:bot board’s barrel jack.
- Connect your micro:bit module to your computer with a USB cable.
Software Setup
- In a Google Chrome or Microsoft Edge browser, go to python.microbit.org to open the micro:bit Python Editor.
- Make sure the cyberbot.py module is added to the Project Files.
(See Add modules to your micro:bit).
Example Script: test_left_ir
This script only tests the cyber:bot’s left IR detector. Focusing on only one of the two object detector circuits at a time helps simplify trouble-shooting. This is yet another example of subsystem testing. After the subsystems check out, we can move to system integration. But first, let’s make sure to test and correct any wiring or code entry errors that might have crept in.
- Set the project’s name to test_left_IR, enter the script below, and then click Save.
(See Save & Edit Scripts and Flash Scripts with Python Editor.) - Click Send to micro:bit.
(See Flash Scripts with Python Editor.)
#test_left_IR
from cyberbot import *
while True:
irL = bot(14, 13).ir_detect(37500)
bot(20).write_digital(irL)
- Position your cyber:bot so that there is nothing close by directly in front of it.
- Set the cyber:bot board’s PWR switch to position 1.
- Check the cyber:bot board. The LED labeled P20 should turn on.
- Place an object, such as your hand or a sheet of paper, a couple of inches (5 cm) from the left object detector. The P20 LED should turn off.
- Move the object away again. The P20 LED should turn on.
- Once the LED is working properly for object not detected and object detected, move on to the Try This and Your Turn sections.
Try This – Test the Right IR Detector
Now it is time to modify the script to test the right-side object detector.
- Change the project name from test_left_IR to test_right_IR.
- Change bot(14, 13) to bot(1, 2).
- Change irL to irR.
- Change bot(20).write_digital(irL) to bot(21).write_digital(irR).
- Repeat the testing steps in this activity for the cyber:bot’s right IR object detector.
- If necessary, troubleshoot any mis-wired circuits or code entry errors.
Your Turn – Test Both Sides Together
The script below combines the right and left IR detector tests into a single script that tests both object detectors.
- Change the project name from test_right_IR to test_both_IR_indicators.
- Update the script so that it matches the one below, and then click Save.
- Click Send to micro:bit.
- Make sure the cyber:bot board’s PWR switch is in position 1.
- Verify that the speaker makes a clear, audible tone.
- Verify that when you place an object in front of the left IR detector, the left (pin 20) LED turns off.
- Repeat the test for the right IR detector and pin 21 LED.
#test_both_IR_indicators
from cyberbot import *
bot(22).tone(3000, 1000)
while True:
irL = bot(14, 13).ir_detect(37500)
irR = bot(1, 2).ir_detect(37500)
bot(20).write_digital(irL)
bot(21).write_digital(irR)
Setting PWR switch to 0 vs. Unplugging Battery Holder
Taking a break, building a circuit, or writing a script?
- Always set the cyber:bot board’s PWR switch to 0 until it’s time to test the next script.
Whenever you are done for the day, always follow these steps.
- Set PWR to 0.
- Unplug the battery holder’s barrel plug from the cyber:bot board’s barrel jack.
