Remember and Use Values
Variables
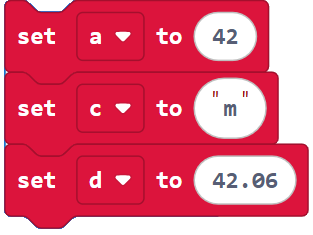
Variables are names you can create for storing, retrieving, and using values in the microbit module’s memory. Here are three example variable declarations from the next program:
A variable can hold different kinds of values, such as integers (whole numbers), decimal numbers, and characters. Each of these kinds of values uses a different data type.
The declaration a = 42 creates a variable named a. The value 42 is an integer, so Makecode automatically assigns the int data type to the a variable, and gives a an initial value of 42.
Next, c = “m” declares a variable named c and initializes it to the value “m.” Since “m” is a character, Makecode assigns c the data type str for storing strings or text.
Then, d = 42.06 declares a variable named d. The value 42.06 is a decimal number, so Makecode assigns d the data type float, which can hold floating-point decimal values.
Example project: variables
Now that you know how code can store values to memory, how can it retrieve and use them? One way is to simply pass each variable to a method’s parameter.
Here is an example, where show string uses the display to scroll the value of the variable inside the parentheses.
- Enter, name, and flash the project variables to your micro:bit.
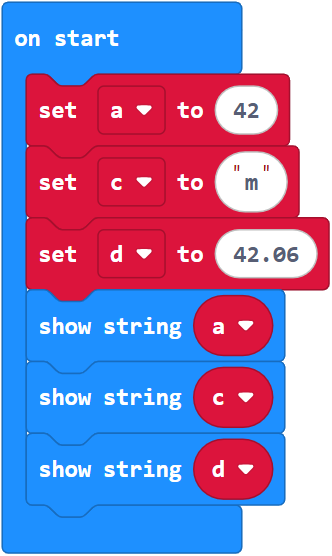
The display will scroll the number 42, then it will scroll the letter m (shown below), and then it will scroll the number 42.06.