Displaying Shapes
The Color OLED module displays shapes as well as text and numbers. This means that you can create images on the OLED’s screen, and you can use those images for anything you can imagine: art, graphics, icons, math functions, user interfaces – the only limit is your imagination!
Example Program – Random Pixels
The easiest thing to draw is a single pixel! The following program will draw 100 random pixels.
- In BlocklyProp Solo, make a new project for your board.
- Build the project shown below.
![]()
- Save the project, and then click the Run once button.
- Your output should look something like this:
![]()
How it Works
The random number blocks provide a random value between 0 and the maximum screen dimension, given by the OLED max height and OLED max width blocks. These numbers are then used to set the position of the pixel drawn by the OLED draw pixel block. This then repeats 100 times, drawing 100 different pixels on the Color OLED’s screen. The pause 20 block slows down the process just enough so you can see the pixels appear individually instead of all at once.
Example Program – Drawing Lines
To draw a line, you need to define a start and an end point – the OLED draw line block takes two x/y coordinates:

The following program will draw 10 different lines.
- In BlocklyProp Solo, make a new project for your board.
- Build the project shown below.
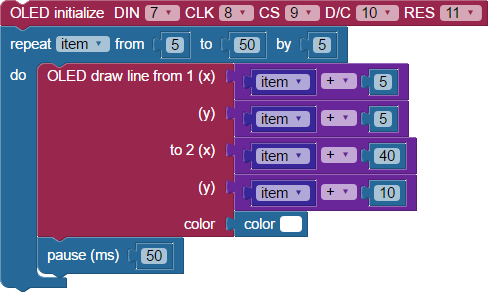
- Save the project, and then click the Run once button.
- Your output should look something like this when the program is finished.
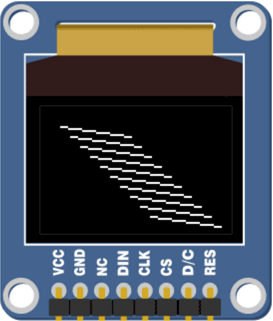
Experiment with the program above by drawing lines of different lengths and colors.
Did You Know?
Taking Shape — In addition to pixels and lines, there are blocks that draw circles and triangles. Each shape has both a color and a fill setting that can be changed, but the shapes themselves are defined differently:
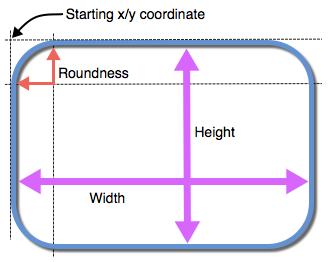
- Rectangles are defined by the coordinates at the top left corner, height, width, and corner roundness.
- Circles are defined by the coordinates at the center of the circle and its radius.
- Triangles are defined by coordinates for each of their three corners.
Out of Bounds — Lines and shapes can start “out of frame” where start or end points are outside of the screen’s view. For example, you could draw a line from (-5,-5) to (150,200) – both points are off-screen.
Try This – Draw a Rectangle
Let’s try a program that will draw a rectangle and demonstrate its corner option. Every second, it will clear the screen and redraw the rectangle with increasing corner roundness.
- In your BlocklyProp account, make a new project for your board.
- Build the project shown below.
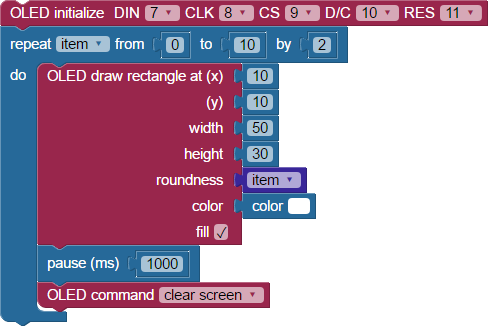
- Save the project, and then click the Run once button.
- Your output should start like the image on the left, and then transform to the image on the right.
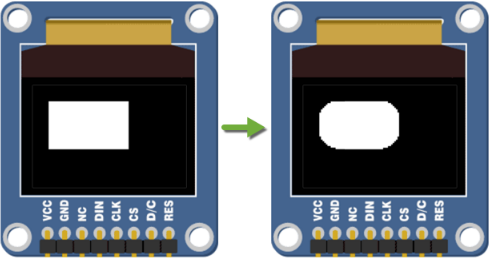
Notice that initially, the rectangle had no roundness at all (square corners). By the end of the program, the corners were very rounded.
Your Turn
- Experiment by changing the program above to draw rectangles with different sizes, positions, colors and roundness.
- Try drawing rectangles that are not filled (outline) by unchecking the “fill” checkbox on the OLED draw rectangle block.
- Try drawing a circle.
- Try drawing a triangle.
- Overlap several different shapes, drawn in different colors. You are making modern art!
