Activity 2: Measure Light Levels Over a Larger Range
The circuit in the previous activity only works over a limited light range. You might get the Activity #1 circuit all nice and calibrated in one room, then take it to a brighter room and find that all the voltage measurements will sit at the maximum value. Or, maybe you’ll take it into a darker room, and the voltages will end up never making it past 0.1 V.
This activity introduces a different phototransistor circuit that the Arduino can use to measure a much wider range of light levels. This circuit and sketch can return values ranging from 0 to over 75,000. Be aware: this time the smaller values indicate bright light, and large values indicate low light.
Introducing the Capacitor
A capacitor is a device that stores charge, and it is a fundamental building block of many circuits. Batteries are also devices that store charge, and for these activities it will be convenient to think of capacitors as tiny batteries that can be charged, discharged, and recharged.
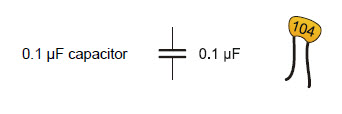
How much charge a capacitor can store is measured in farads (F). A farad is a very large value that’s not practical for use with these BOE Shield-Bot circuits. The capacitors in your kit store fractions of millionths of farads. A millionth of a farad is called a microfarad, and it is abbreviated μF. This one stores one tenth of one millionth of a farad: 0.1 μF.
Common Capacitance Measurements
microfarads: (millionths of a farad), abbreviated μF 1 μF = 1×10-6 F
nanofarads: (billionths of a farad), abbreviated nF 1 nF = 1×10-9 F
picofarads: (trillionths of a farad), abbreviated pF 1 pF = 1×10-12 F
The 104 on the 0.1 μF capacitor’s case is a measurement in picofarads or (pF). In this labeling system, 104 is the number 10 with four zeros added, so the capacitor is 100,000 pF, which is 0.1 μF.
(100,000) × (1 × 10-12) F = (100 × 103) × (1 × 10-12) F
= 100 × 10-9 F = 0.1 × 10-6 F
= 0.1 μF.
