How it Works
How the Pushbutton Works
Looking inside the pushbutton, the legs that stick out of both sides of the pushbutton’s body are actually wires that pass all the way through. One of the wires forms legs 1 and 4, and the other forms legs 2 and 3. The button has a metal bar attached underneath and a springy material that keeps it floating above the two wires. When you press the button, the metal bar comes to rest atop the two wires.
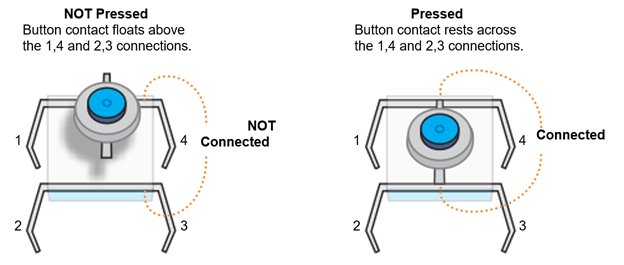
Since legs 1 and 4 are actually part of a single wire, they are always electrically connected, so a micro:bit continuity test will always display the checkmark. The same applies to legs 2 and 3.
When the button is not pressed, current cannot conduct between the 1,4 and 2,3 legs, so its connection is called open or an open circuit. When the button is pressed, current can conduct between the 1,4 and 2,3 legs, and the connection is called closed. Since this pushbutton is open when it is not pressed, it is called a normally open pushbutton. Though your kit does not have them, normally closed pushbuttons also exist, where their connection is closed when it is not pressed, and open when it is pressed.
When the button is not pressed, legs 1 and 4 are insulated from 2 and 3. So probing any of these pairs of pins will result in the micro:bit continuity tester’s LED display showing the not connected X: (4, 3), (4, 2), (1, 2), (1, 3). When you press and hold the pushbutton, the micro:bit continuity tester displays the connected checkmark instead.
Try This
In addition to checking pushbutton functionality with continuity tests, sometimes the voltage it applies to the micro:bit needs to be checked. In prototype tests and machine repairs, this is one of the first tests when pressing a button does not produce the desired result.
- Right-click measure_volts_with_cyberscope and select Save link as… to download it.
measure_P6_volts_with_cyberscope.hex
- Go to python.microbit.org/v/2.
- Click Load/Save and then drag the file you just downloaded and drop it on the gray box in the Load section.
- Click the Flash button to load the script into the micro:bit.
- Click Disconnect.
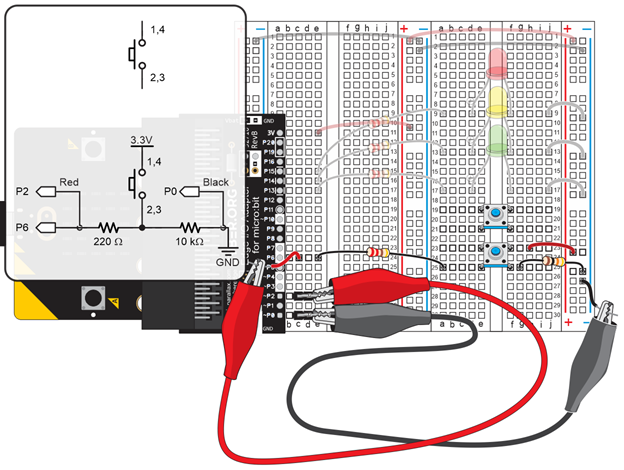
- Go to cyberscope.parallax.com and click Connect.
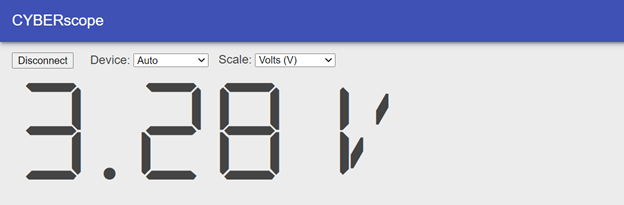
- Press and hold the pushbutton for several seconds and verify that the voltage measurement is close to 3.3 V.
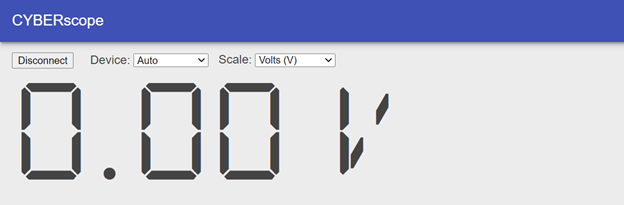
Release the pushbutton and verify that the measurement returns to a value close to 0 V.
- In the CYBERscope, click Disconnect.
