Infrared Object DetectionCopy
This infrared detection system is kind of like an infrared flashlight. If the invisible beam from the IR LED reflects off an object and is picked up by the IR receiver, it’ll send a low signal. Otherwise, it sends a high signal. One thing about the infrared beam, it has to be flickering on/off at 38 kHz (38,000 times per second) for the IR detector to “see” the reflection.
Parts
(1) LED shield 350-90005
(1) LED standoff 350-90004
(1) IR LED 350-00003
IR Receiver 350-00039
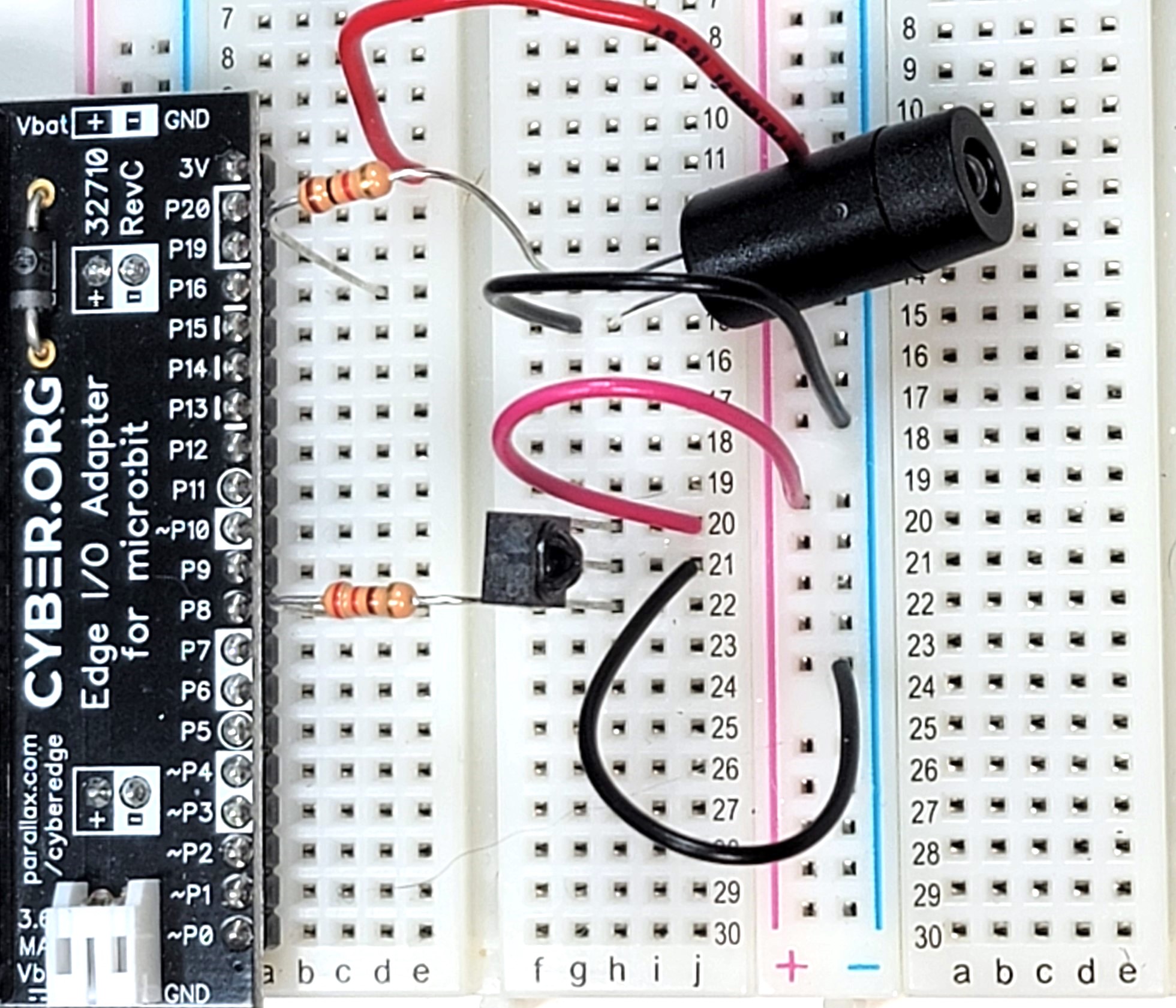
(1) 2 kΩ resistor (red-black-red-gold
(1) 220 Ω resistor (red-red-brown-gold)
Jumper wires: Red, (2) black
Schematic
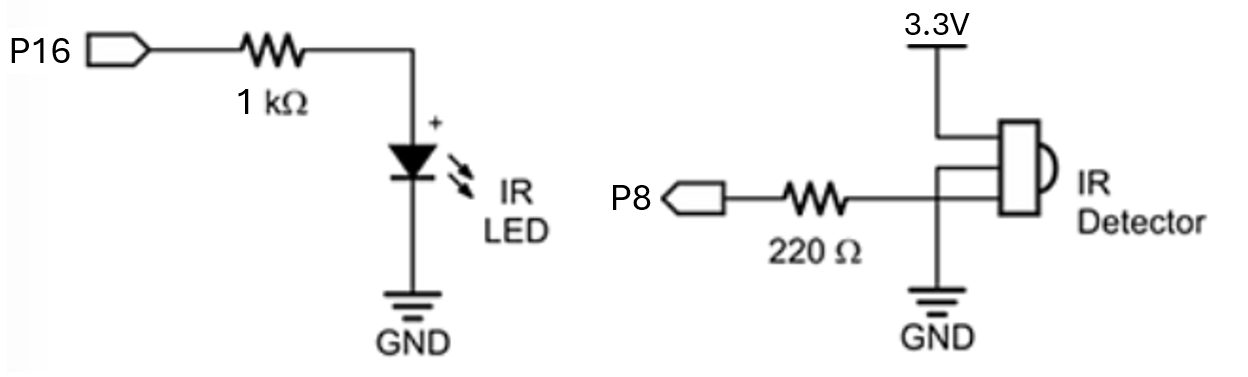
Wiring
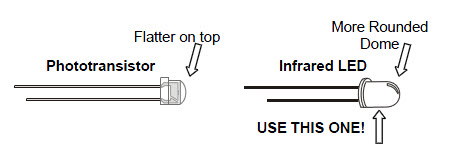
Make sure you are using an infrared LED and not phototransistors. The infrared LED has a taller and more rounded plastic dome:
Assemble the IR Headlight
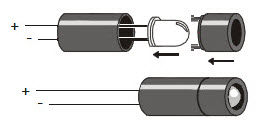
The infrared LED is designed to sit in the standoff tubes a certain way. The flat spot on the LED dome matches a flat ledge inside the tube. Holes on the bottom of the tube are labeled for the anode (+) and cathode (-) leads.
- Insert the infrared LED into the LED standoff tube, threading the anode and cathode leads through their respective holes in the bottom. If properly aligned, the LED should drop in place without pushing.
- Slip the short tube over the IR LED’s clear plastic case, tab end first. The tabs should snap into the standoff, holding the LED in place.
Breadboard Connections
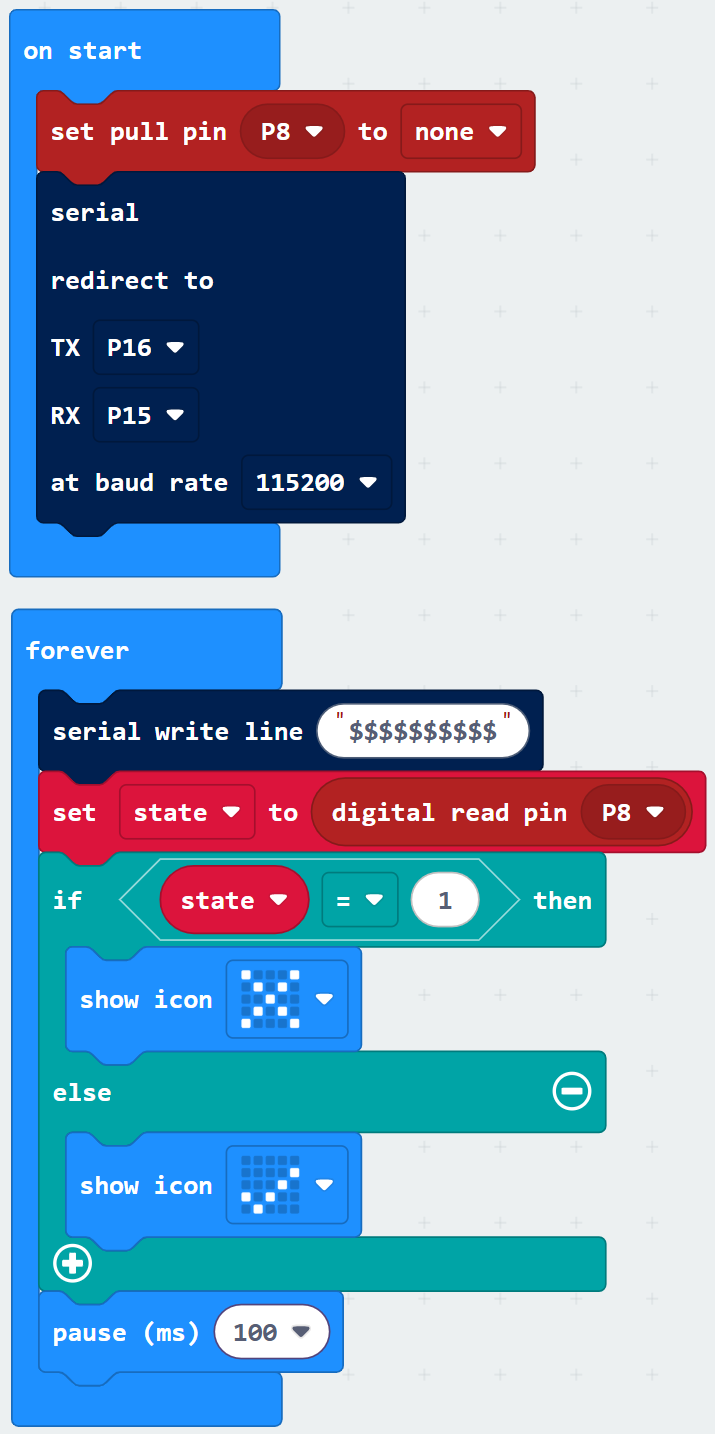
Script
Tests
Face an object like a box, your hand, or a piece of paper so that the infrared LED shines light at it. The distance should be 6 inches or less. The micro:bit should respond by displaying a checkmark. Take the object away, and the micro:bit should respond by displaying an X.