Other Useful Methods
This example program introduces four more useful string methods: replace(), upper(), lower(), and split().
Example script: other_methods_intro
- Enter, name, and save other_methods_intro.
- Click the Send to micro:bit button.
# other_methods_intro
from microbit import *
sleep(1000)
string = "This is a string. It is a sequence of characters!"
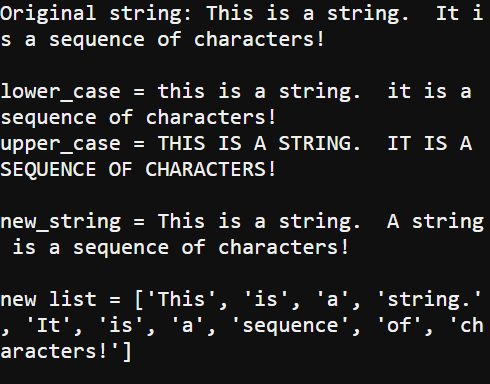
print("Original string:", string)
print()
lower_case = string.lower()
upper_case = string.upper()
print("lower_case =", lower_case)
print("upper_case =", upper_case)
print()
new_string = string.replace("It", "A string")
print("new_string =", new_string)
print()
new_list = string.split()
print("new list =", new_list)
print()
- Check the results in the serial monitor.
- Verify that it displays the original string, the lower and uppercase versions, a version that replaced “It” with “A string”, and a list with all the substrings that were separated by spaces in the original.
How other_methods_intro Works
The first routine declares a string, names it string, and then prints it for reference.
string = "This is a string. It is a sequence of characters!"
print("Original string:", string)
print()
The string.lower() and string.upper() methods return lower and upper case versions of the original string, and print them:
lower_case = string.lower()
upper_case = string.upper()
print("lower_case =", lower_case)
print("upper_case =", upper_case)
print()
The string.replace() method is another way to replace parts of a string. It’s not as straightforward as the approach from the previous String Surgery section, because it would replace all instances that matche the substring, if there were more than one “It”.
new_string = string.replace("It", "A string")
print("new_string =", new_string)
print()
The string.split() method splits a string with separators into substrings. By default, the separator is a space, but you could pass it a comma, for example. Many data strings are comma delimited, and need to be split before each individual data item can be examined.
new_list = string.split()
print("new list =", new_list)
print()
