String Features: Indexing, Functions, Methods
Each character in a string has an index number. That index starts at the first character, counting from zero.
For example, in s = “Hello string”, H has an index of 0, e has an index of 1, l has an index of 2, and so on, up through g with an index of 11. See how even the space between Hello and string is a character with an index?
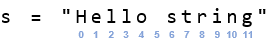
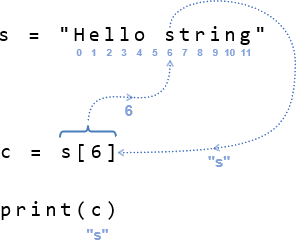
Python has many tools for accessing, manipulating, and converting string information. Here is one indexing example where the 6th character ’s’ is copied to the c variable and then printed.
Python has built-in functions for certain string operations:
- ord() — Returns the ASCII value of a character
- chr() — Returns the character of an ASCII value
- len() — Returns the length of a string
- str() — Converts other types of objects to string
Additionally, strings that represent other data types can be converted to those types with built-in functions like int(), float(), dict(), list() and more. Example:
s = "123" # A string with numbers, but cannot be used in calculations n = int(s) # Convert to an int type n = n + 1 # The result can be used in calculations
The string class has many methods. Some return information about the string. Others return new strings that are changed versions of the originals, and there are also some that return different types of objects that contain the string’s characters. A few examples are shown below.
- Given the example string shown, can you anticipate what each variable would look like printed?
string = "This is a string. It is a sequence of characters!"
char_index = string.find("sequence") # returns index of first letter in sequence
new_string = string.replace("It", "A string") # replaces "It" with "A string"
char_list = list(string) # converts a string into a list
lower_case = string.lower() # converts string to all lower case
upper_case = string.upper() # converts string to all upper case
