Try This: Access Substrings
In the previous activity, a single character was accessed using an index, like c = s[3]. Your scripts can also view segments of strings by using a range instead of a single index number in the square brackets.
Let’s say you have a string named s:
- s[5] — fifth character in a string
- s[3:7] — third through sixth characters in a string
- s[:5] — beginning through the fifth character
- s[11:] — eleventh character through the end of the string.
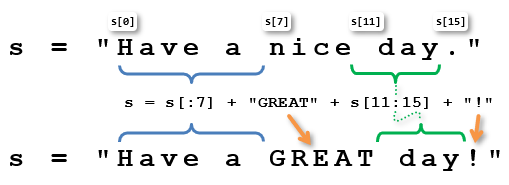
In Python-speak, strings are considered immutable. Being immutable means that once created, a string cannot be changed. That doesn’t mean that s = “Have a nice day.” cannot be changed to s = “Have a GREAT day!” It just means that the original “Have a nice day.” string cannot be changed. A statement can still grab parts of “Have a nice day.” and use them to create a new string that reads “Have a GREAT day!” The resulting string can even be assigned back to s.
s = "Have a nice day." # BEFORE s = s[:7] + "GREAT" + s[11:15] + "!" s = "Have a GREAT day!" # AFTER
The s variable starts as this string: “Have a nice day.” The second line adds “Have a ” + “GREAT” + ” day” + “!”. See how “Have a “ is s[:7] from the original string? Add the string “GREAT” to that, and then ” day” with a leading space, which is s[11:15], and lastly add “!”, and the string surgery is complete!
Example script: string_surgery_try_this
This script starts with “Have a nice day.” and then creates a new string sn with the “nice” portion of the original. After that, it demonstrates some more ways to access segments of an original string that were introduced above.
- Enter, name, and save string_surgery_try_this.
- Click the Send to micro:bit button.
# string_surgery_try_this
from microbit import *
sleep(1000)
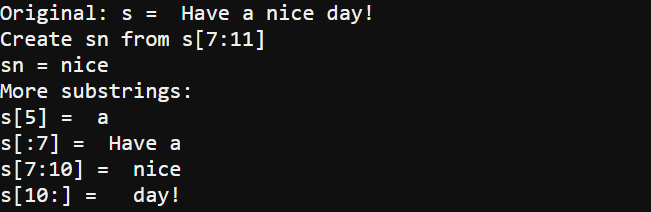
s = "Have a nice day!"
print("Original: s = ", s)
sn = s[7:11]
print("Create sn from s[7:11]")
print("sn =", sn)
print("More substrings:")
print("s[5] = ", s[5])
print("s[:7] = ", s[:7])
print("s[7:10] = ", s[7:11])
print("s[10:] = ", s[11:])
- Check the results in the serial monitor.
- Verify that it displays:
The original string: s = Have a nice day!
Create sn from s[7:11] sn = nice
More substrings:
s[5] = a
s[:7] = Have a
s[7:10] = nice
s[10:] = day!