String Features: Indexing and Blocks
Each character in a string has an index number. That index starts at the first character, counting from zero.
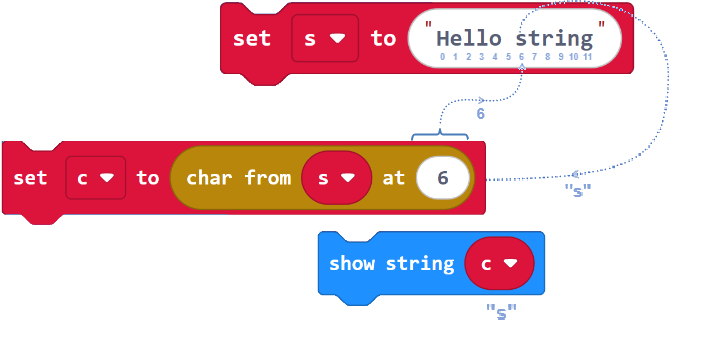
For example, in s = “Hello string”, H has an index of 0, e has an index of 1, l has an index of 2, and so on, up through g with an index of 11. See how even the space between Hello and string is a character with an index?

Makecode has many tools for accessing, manipulating, and converting string information. Here is one indexing example where the 6th character ‘s’ is copied to the c variable and then printed.
Additionally, strings that represent other data types can be converted to those types with built-in blocks. Example:

