Navigating by Touch
In previous navigation programs, our projects only made the cyber:bot execute a list of movements predefined by you, the programmer. Now that you can create a project to make the cyber:bot monitor whisker switches and trigger action in response, you can also create a project that lets the cyber:bot drive and select its own maneuver if it bumps into something. This is an example of autonomous robot navigation.
Whisker Navigation Overview
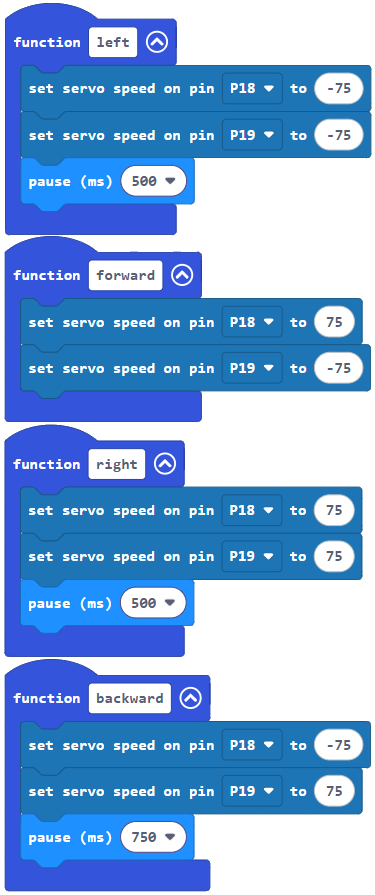
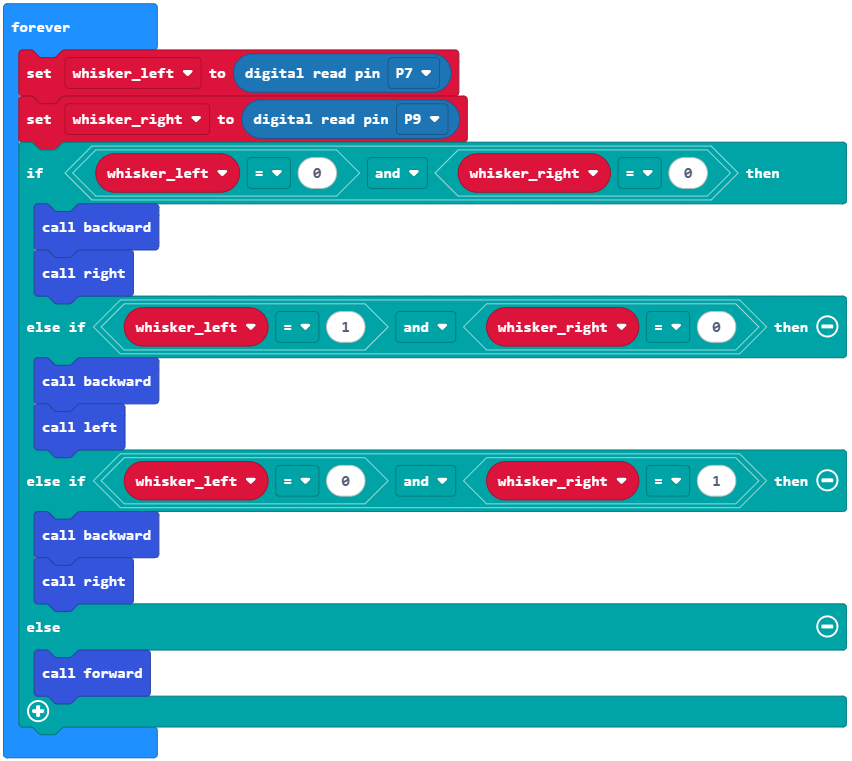
The roaming_with_whiskers project makes the cyber:bot go forward while monitoring its whisker inputs, until it encounters an obstacle with one or both of them. As soon as the cyber:bot senses whisker electrical contact, it uses an if…else if…else statement to decide what to do. The decision code checks for various whisker pressed/not pressed combinations, and calls navigation functions to execute back-up-and-turn maneuvers. Then, the cyber:bot resumes forward motion until it bumps into another obstacle.
Example Project: roaming_with_whiskers
Let’s try the project first, and then take a closer look at how it works.
- Set the cyber:bot board’s 3-position power switch to position 1.
- Enter and flash the project roaming_with_whiskers.
- Disconnect the cyber:bot from its programming cable, and set the power switch to 2.
- Put the cyber:bot on the floor, and try letting it roam. When it contacts obstacles in its path with its whisker switches, it should back up, turn, and then roam in a new direction.