Inertia, Momentum, Impulse, and Kinetic Energy
Forces change an object’s motion, but without them, an object will keep doing whatever it was doing. If the object is not moving, it will stay in place. If an object is moving, it will keep moving at the same speed in the same direction forever unless a new force changes or stops its motion. An object’s tendency to keep doing whatever it is doing is called inertia. An object’s mass determines how much inertia it has. In fact:
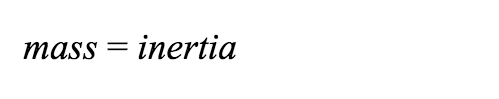
Once an object is moving, it takes some force to stop it or change its motion. The more velocity it has, the more force it takes to stop. In addition, the more mass an object has, the harder it is to stop. The combination of mass and velocity is called momentum:
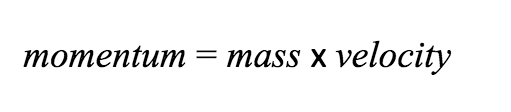
Momentum is a measure of how much movement an object has, and knowing an object’s momentum can help you determine how much force it will take to stop or change the direction of a moving object. Changing the motion of an object requires a force to be applied for a certain amount of time. A force applied for an amount of time is called an impulse:
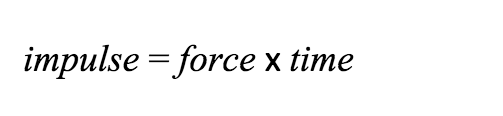
Imagine pushing a car in neutral. If you push with 10 pounds of force for 10 seconds, or push with 100 pounds of force for 1 second, the speed it will end up moving with will be the same. An impulse applied to an object gives it momentum. In fact, an impulse results in a change in momentum:
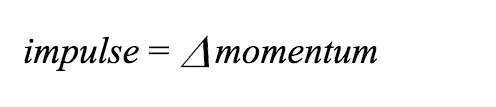
What momentum doesn’t help determine is how much energy is contained in the movement of an object. An object’s Kinetic Energy is determined by half of its mass times the square of its velocity:
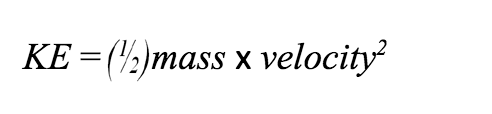
Because the velocity is squared (times itself again), an object that is moving 100 miles per hours has 4 times as much kinetic energy as an object that is only moving 50 miles per hour. This is important to know because it is an object’s kinetic energy that describes things like how long it will take to stop and how much damage it will do in a collision.
Educators: Additional Lessons and Resources are available on Khan Academy here: Impacts and linear momentum, and practice problems can be found by searching online for “momentum and impulse practice problems“
