Navigate by Light
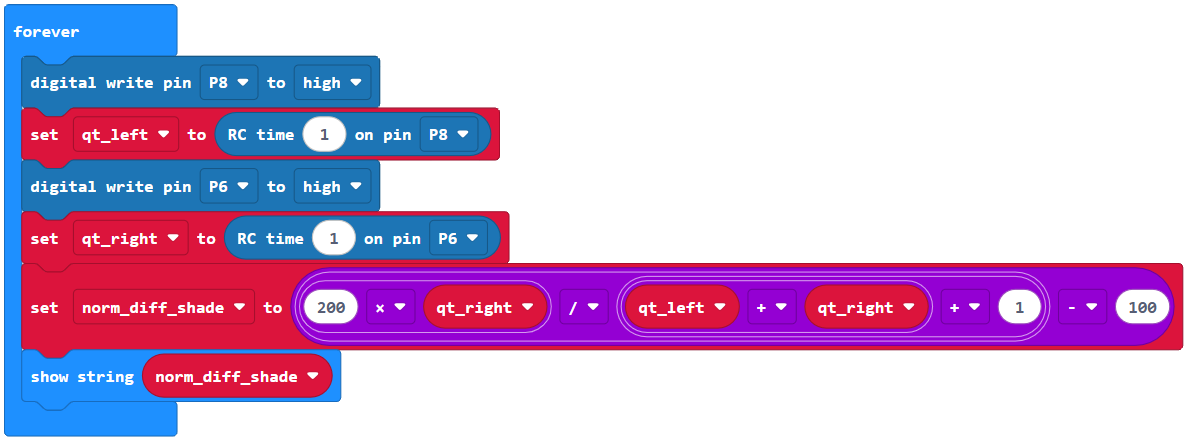
Normal Differential Shade Values for Roaming
To make the cyber:bot roam toward light, the code’s job is to get from the raw sensor values to a norm_diff_shade value that can be used to adjust the servo speeds. We want cyber:bot to turn a little—or a lot—when the contrast between the light detected on each side is a little—or a lot. The following equation in code makes the norm_diff_shade value to integer between -100 and 100.

Let’s confirm this strategy works before using it in a navigation project.
Example project: test_integer_shade_value
- Enter and upload test_integer_shade_value.
- Cover any windows letting in direct light, so the sun doesn’t overwhelm the phototransistors.
- Put the cyber:bot board’s power switch in position 1.
- Cast shade over each photoresistor, and also try a flashlight if you have it, and watch the values on the micro:bit display.
Make sure the micro:bit should display values between -100 and 100 depending on which sides the light and shadow are on. The values do not necessarily have to reach the -100 and 100 end points, but they should get close.
Shady Navigation Decisions
Now, using this new strategy, we can manipulate the servos to drive based on which direction the light is hitting the cyber:bot. The light-seeking project and some ideas for adapting it are included below. How this project works is on the next page.
- Enter and flash the project seek_bright_light.
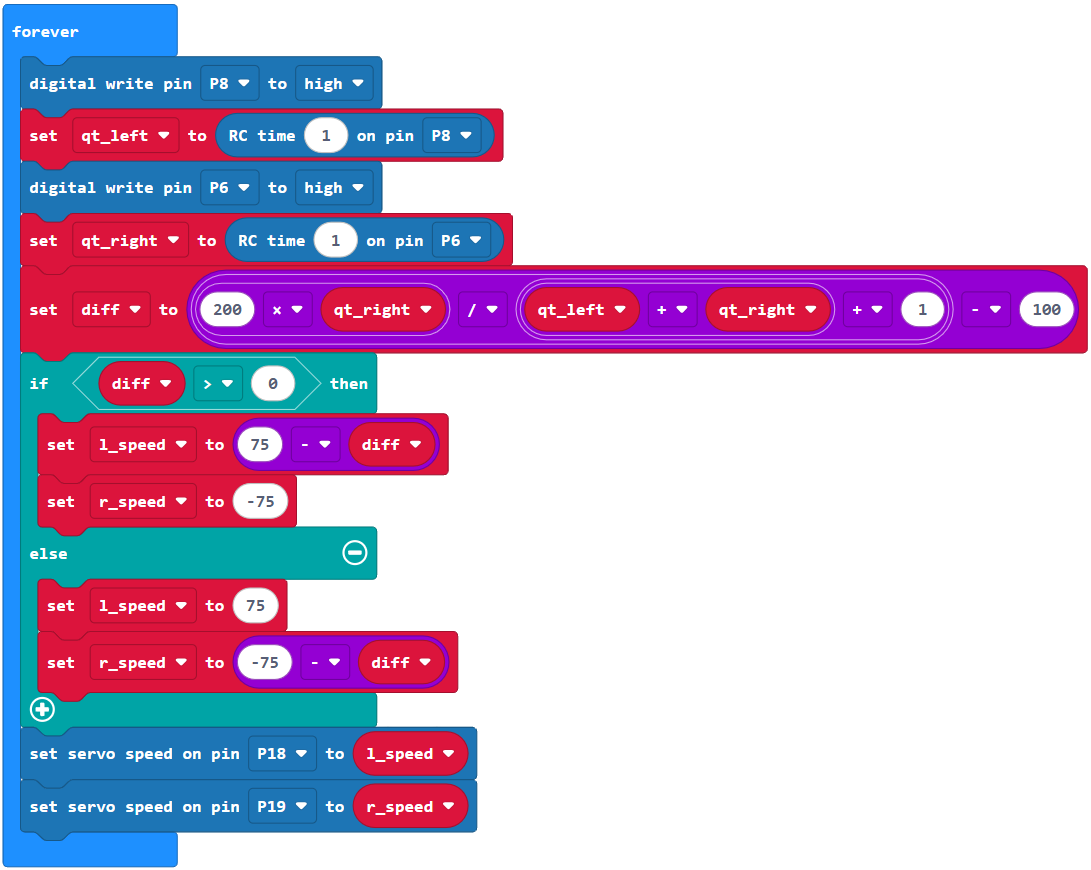
- Put the cyber:bot power switch in Position 2. The cyber:bot should start moving towards the brightest area of the room.
- Cast shade over one phototransistor, then over the other. The cyber:bot should turn away from from the shaded side.
- Use a flashlight to drive the cyber:bot and verify that the cyber:bot is navigating towards the bright light.
- If it is not working, check the project and the wiring to make sure everything is correct.
Try This: Changing Responsiveness
You can change the cyber:bot’s responsiveness by changing the value 200 in this block of the project:

- To increase responsiveness to light, change 200 to a larger value and re-flash the project. Does the cyber:bot’s behavior change?
- To decrease responsiveness, change 200 to a smaller value and re-flash the project. Now how does the cyber:bot behave?
Your Turn
Here are several more light-sensing navigation ideas for your cyber:bot that can be made with adjustments to the forever block:
- To make your cyber:bot follow shade instead of light, place norm_diff_shade = -norm_diff_shade right before the if statement.
- End roaming under a bright light or in a dark cubby by detecting very bright or very dark conditions. Add qt_left and qt_right together, and compare the result to either a really high (dark) threshold value or a really low (bright) threshold value.
- Make your cyber:bot function as a light compass by remaining stationary and turning toward bright light sources.
