Metric Prefixes to Values Conversion Script
This script converts quantities and metric prefixes to the numbers they represent.
Example Script: metric_prefixes_to_values
- Enter the metric_prefixes_to_values script into the micro:bit Python Editor.
- Set the project name field to metric_prefixes_to_values, then click Save.
- Click Send to micro:bit.
# metric_prefixes_to_values
prefix_exponents = {'M':6, 'k':3, 'm':-3, 'u':-6}
print("Enter quantity, metric prefix, and unit.")
print("Result will be a decimal value.")
print()
while True:
text = input("Enter quantity: ")
quantity = float(text)
prefix = input("Enter metric prefix: ")
exponent = prefix_exponents[prefix]
unit = input("Enter unit: ")
value = quantity * (10 ** exponent)
digits = str(abs(exponent) + 1)
if value < 1:
fstr = "%." + digits + "f"
else:
fstr = "%" + digits + ".0f"
print("Value:", fstr %value, unit)
print()
Conversion Script Tests
This script converts quantities and metric prefixes to the numbers they represent.
- Click Show serial.
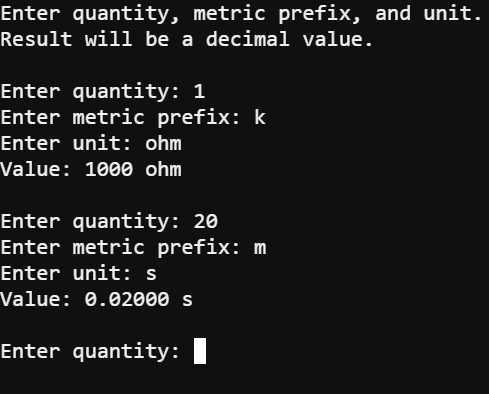
(See Use the Serial Monitor.) - Click to the right of the Enter Quantity prompt, type 1 and then press the Enter key.
- Continue typing the values in the image below to the right of each prompt, and press Enter after each one.
Experiment with Other Values
Here are some you will see in upcoming lessons.
- Experiment with other values, using the expressions on the left, like 50 ms, 38 kHz and so on. Substitute ohm for Ω and u for µ.
- t = 50 ms — time is 0.050 seconds
- f = 38 kHz — frequency of 38,000 repetitions per second. Because of the micro:bit module’s 32-bit floating point math, you might get a value like 37999 instead.
- I = 1.1 mA — current is 0.0011 amps
- V = 5 mV — voltage is 0.0050 V
- R = 1 kΩ — resistance is 1000 ohms
- C = 10 µF — capacitance is 0.000010 farads