To properly power the servos, you’ll need to switch to an external battery pack now. When servos make sudden direction changes or push against resistance to rotation, they can draw more current than a USB port is designed to supply. Also, it would be no fun for the BOE Shield-Bot to be tethered to the computer forever! So, from here on out we’ll be using an external battery pack with five 1.5 V AA batteries. This will supply your system with 7.5 V and plenty of current for the voltage regulators and servos. From here forward, remember two things:
- ALWAYS unplug the battery pack when you are done experimenting for a while. Even when the power switch on your BOE Shield is off (position-0), the Arduino module will still draw power from the batteries.
- Unplug the programming cable too, whenever you unplug the battery pack. That way, you won’t accidentally try to run the servos off of USB power.
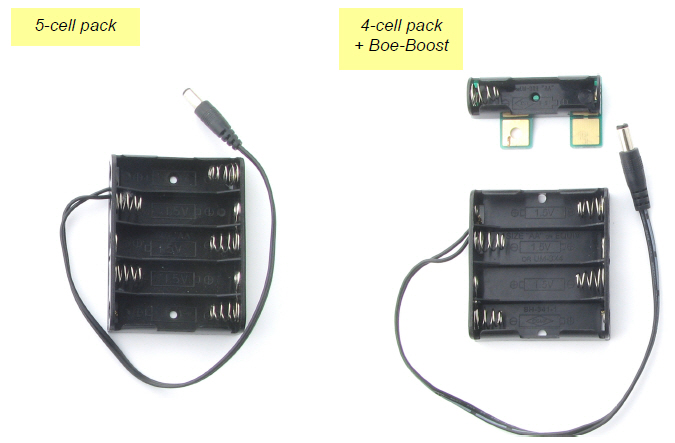
Which Battery Pack Do You Have?
- Compare your parts to the picture below to see which battery pack you have.
- For the 5-cell Pack, keep going on the next page.
- For the 4-cell pack, skip to the 4-Cell Pack + Boe-Boost Setup.
Rechargeable Options
The thrifty Boe-Boost (#30078) allows you to add another cell in series with a 4-cell or 5-cell pack. Adding a 6th 1.2 V AA rechargeable cell to a 5-cell pack will supply 6 x 1.2 = 7.2 V.
The Li-ion Boe-Bot Power Pack-Charger (#28988) combines a lithium-ion battery pack and recharger in one board that you can mount under your Shield-Bot.
CAUTION: AC powered DC supplies are not recommended for the BOE Shield-Bot.
Some DC supplies provide much higher voltage than their rating. The BOE Shield-bot is designed for use with a 7.2–7.5 V battery supply. It will work with higher supply voltages at low loads, but the servo loads can heat up the regulator until it shuts off to protect itself.