How test_gripper_angles_buttons Works
After importing the cyberbot module, the script uses display.show(Image.ARROW_E) to point at the micro:bit module’s B button.
# test_gripper_angles_buttons from cyberbot import * display.show(Image.ARROW_E)
The main loop repeatedly checks if either the A or B buttons have been pressed. If the B button was pressed since the last time it checked, the bot(16).servo_angle(30) call closes and lifts the Gripper paddles. If the A button was pressed since the last time it checked, the bot(16).servo_angle(150) call lowers and opens the Gripper paddles.
Both servo_angle calls can be considered “set it and forget it” so the servo will hold the position it was most recently set to. Whenever a particular button is pressed, the arrow is updated to point at the other button.
while True:
if button_b.was_pressed():
bot(16).servo_angle(30) # close gripper & lift
display.show(Image.ARROW_W)
elif button_a.was_pressed():
bot(16).servo_angle(150) # Lower gripper & open
display.show(Image.ARROW_E)
Try This
Some objects need to be lifted up and set down more carefully, like objects with narrower bases. Try modifying the test script to make the Gripper close-lift and lower-open more gradually.
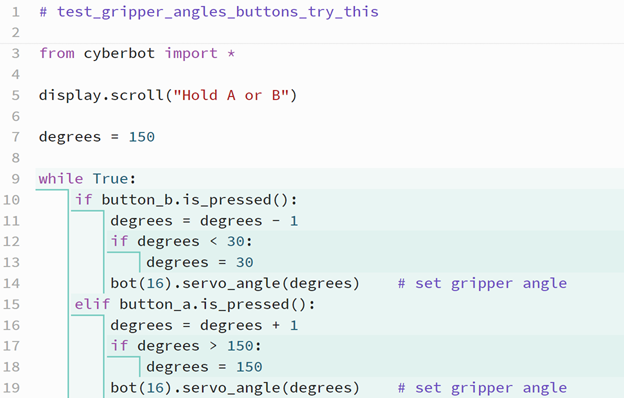
- Set the project name to test_gripper_angles_buttons_try_this.
- Modify the script as shown below.
- Make sure to change was_pressed to is_pressed in the if and elif conditions.
- Save your work by clicking Save.
- Click Send to micro:bit.
- Make sure the batteries and barrel plug are connected and that the cyber:bot board's PWR switch is set to 2.
- Test by holding the B button until the gripper goes all the way up, and then holding the A button until the gripper goes all the way down and opens.