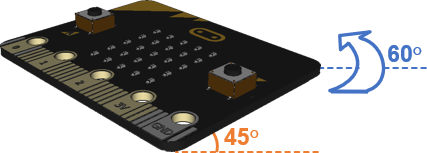
In addition to the rotation angle with opposite and adjacent x and y values, your scripts can calculate the triangle’s hypotenuse to determine how far from vertical the micro:bit has been tilted.
Example script: rotate_angle_with_degree_of_tilt
- Enter, name, and save rotate_angle_with_degree_of_tilt.
- Click the Send to micro:bit button.
# rotate_angle_with_degree_of_tilt
from microbit import *
import math
sleep(1000)
while True:
x = accelerometer.get_x()
y = accelerometer.get_y()
angle = round( math.degrees( math.atan2(y, x) ) )
hyp = round( math.sqrt( x**2 + y**2 ) )
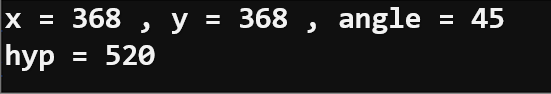
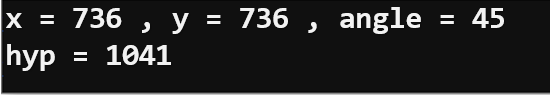
print("x =", x, ", y =", y, ", angle =", angle)
print("hyp =", hyp)
print()
sleep(750)
- Check the results in the serial monitor.
- Hold the micro:bit vertical and pick a rotation angle, like 60°.
- Note the angle and hyp values.
- Start holding the micro:bit vertically, rotated at 45 degrees. Make a note of the hyp variable value. It should be near 1024.
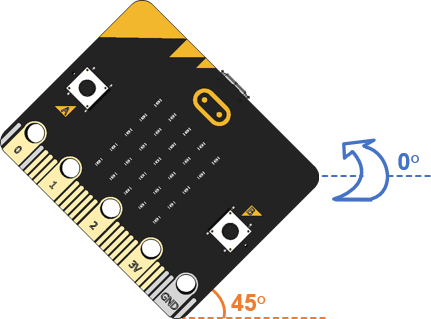
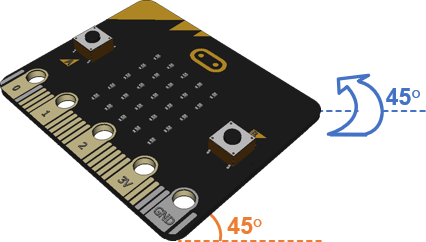
Tilt it 45° degrees away from you (toward level) while keeping the rotation at 45°. The angle should stay the same, but the hyp variable should report a smaller value.
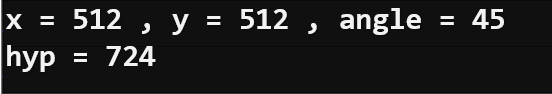
Continuing to hold the rotation at 45°, tilt it a little further toward level. Did the hyp variable value get even smaller?